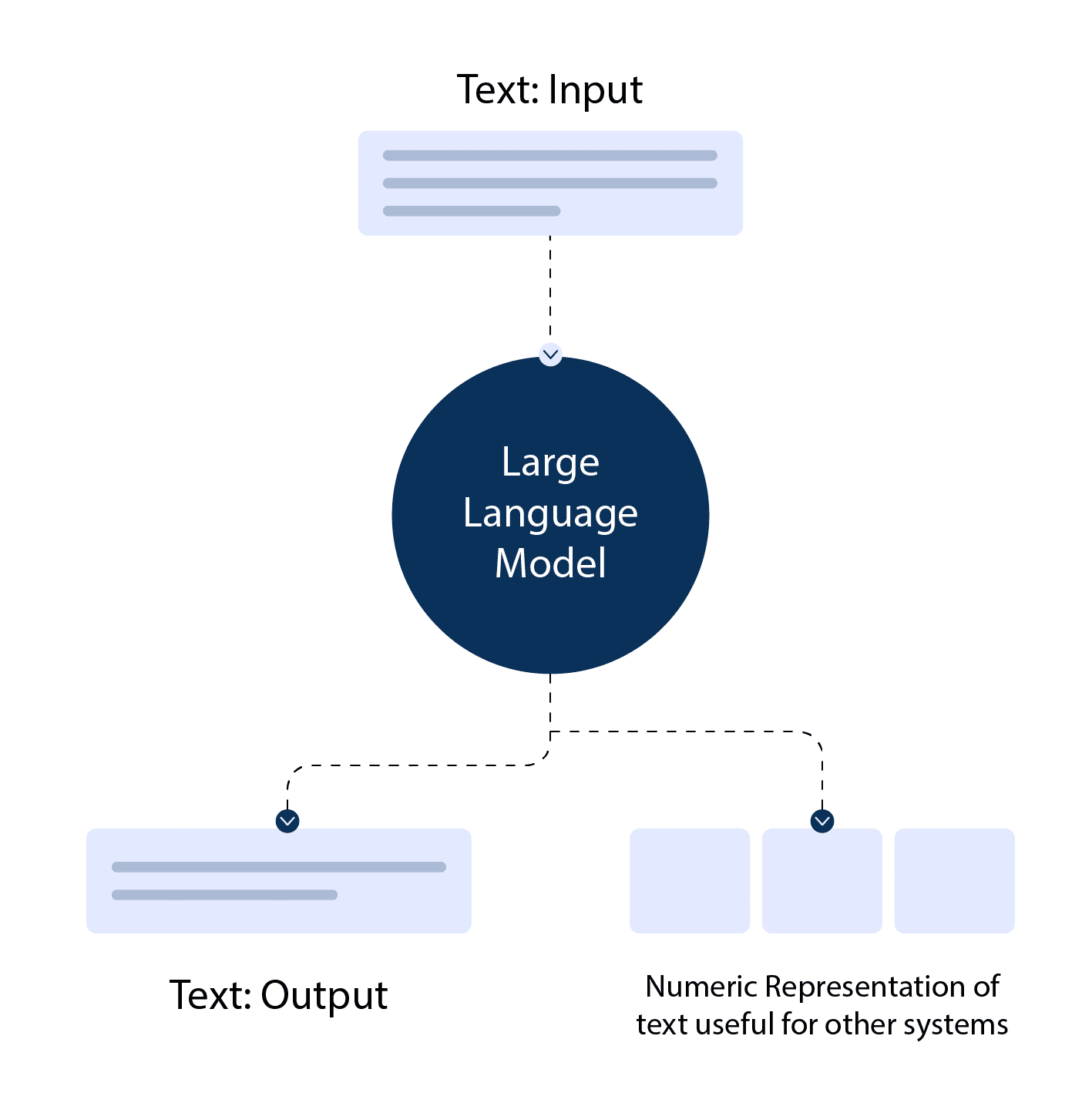
What are Large Language Models?
Large Language Models are advanced machine learning models designed to understand, generate, and manipulate human-like text.
They're often based on deep learning techniques and can process vast amounts of data, enabling them to learn and mimic complex linguistic patterns, context, and semantics.
Language models have come a long way since their inception. They started with simple n-gram models, which predict the next word in a sequence based on the previous n-1 words.
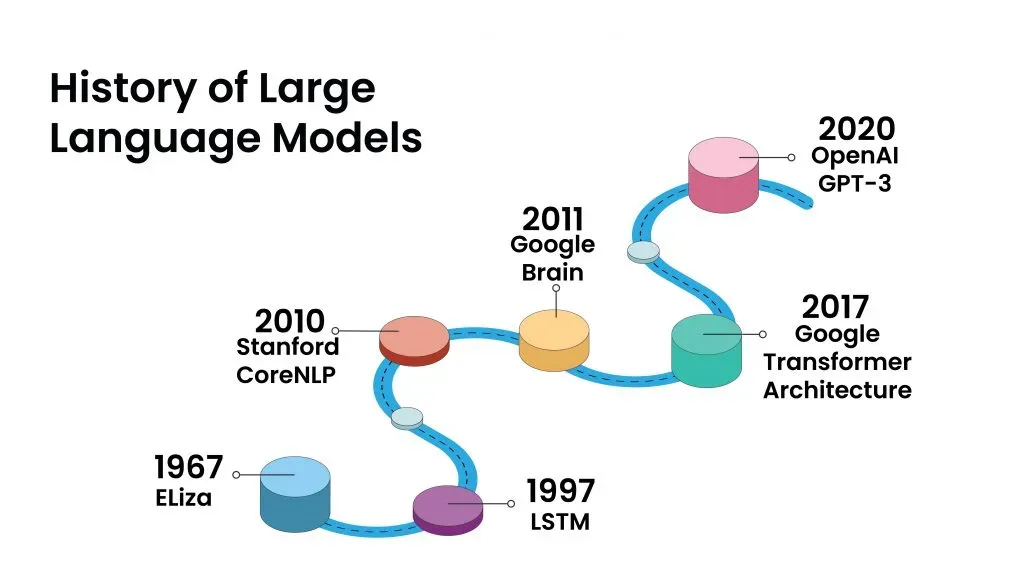
Then came recurrent neural networks (RNNs), which were better at capturing long-range dependencies but struggled with vanishing gradients. The introduction of attention mechanisms and transformers revolutionized large language models, allowing them to process and learn from massive datasets more efficiently.
Large language models have significantly improved natural language understanding and generation capabilities, paving the way for more advanced AI applications. They have become essential tools for various tasks, from sentiment analysis and machine translation to content generation and chatbot development.
Why are Large Language Models Important?
Large language models are important due to their ability to process and generate human-like text, enabling numerous applications and advancements.
Enhanced Natural Language Processing
Large Language Models (LLMs) are pivotal in advancing natural language processing (NLP). These models are adept at understanding context and semantics, making them essential in numerous NLP applications such as language translation, sentiment analysis, and text summarization. Their large size, often containing billions of parameters, allows them to capture subtleties in language that smaller models might miss.
Revolutionizing Human-Computer Interaction
Human-computer interaction has been revolutionized by LLMs. By efficiently processing and generating human-like text, these models pave the way for more intuitive and intelligent conversational agents. Users can interact with devices and applications in natural language, making technology more accessible and user-friendly.
Personalized Content Generation
LLMs can generate high-quality, personalized content in a scalable manner. Whether it's creating tailor-made news summaries, blog posts, or social media content, LLMs can analyze individual preferences and generate content that is both relevant and engaging. This can help organizations and individuals streamline their content creation processes, saving time and resources.
Improving Decision-Making Processes
In the realm of decision-making, LLMs are a game-changer. They can analyze large datasets, extract insights, and provide recommendations. Businesses and governments can use these insights for data-driven decision-making, resulting in better resource allocation, risk mitigation, and efficiency improvements. LLMs can also assist in complex simulations, forecasting, and predictive analytics.
Boosting Educational Initiatives
Education is another domain where LLMs make a significant impact. They can be used to create adaptive learning platforms that cater to the individual needs of students. LLMs can also assist educators in curriculum development and student assessment. Furthermore, they provide a valuable tool for students, helping with research, language learning, and problem-solving skills.
Addressing Multilingual Challenges
With the ability to process and generate text in numerous languages, LLMs play an essential role in bridging linguistic divides. They enable real-time language translation, allowing for seamless communication across borders. Moreover, LLMs facilitate the creation of multilingual content, ensuring that information and services are accessible to a broader global audience.
How do Large Language Models Work?

Architecture and Components
Large language models typically use a transformer architecture, which consists of an encoder and a decoder. The encoder processes the input text, while the decoder generates the output text. Both the encoder and decoder are made up of multiple layers of self-attention mechanisms, which help the model understand the relationships between words in a sequence.
Training Techniques
Training large language models requires massive amounts of text data and computational resources. The models are pre-trained on a large corpus of text, learning to predict the next word in a sentence given the previous words. This pre-training phase allows the model to learn grammar, facts, and reasoning abilities. After pre-training, the model is fine-tuned on a smaller, task-specific dataset to adapt its knowledge to specific tasks or domains.
Fine-tuning and Adaptation
Fine-tuning is the process of adapting a pre-trained large language model to a specific task or domain. This involves training the model on a smaller dataset tailored to the target task, allowing it to learn task-specific nuances and patterns. Fine-tuning is essential for achieving high performance on specialized tasks, such as sentiment analysis in a specific industry or question-answering in a particular domain.
Types of Large Language Models
GPT-3 (OpenAI)
GPT-3, or Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3, is a state-of-the-art language model developed by OpenAI. It consists of 175 billion parameters, making it one of the largest and most powerful language models to date. GPT-3 has shown remarkable capabilities in various tasks, including translation, summarization, and even programming.
BERT (Google)
BERT, or Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers, is a groundbreaking language model developed by Google. Unlike traditional language models that process text in a left-to-right or right-to-left manner, BERT processes text bi-directionally, allowing it to better understand context and semantics. BERT has set new performance benchmarks in numerous natural language processing tasks.
T5 (Google)
T5, or Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer, is another large language model developed by Google. It's designed to convert all NLP tasks into a text-to-text format, making it a versatile and powerful tool for various applications. T5 has demonstrated impressive performance in tasks like translation, summarization, and question-answering.
RoBERTa (Facebook)
RoBERTa, or Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach, is a language model developed by Facebook AI. It's an optimized version of BERT that incorporates several training improvements, such as larger batch sizes, longer training times, and dynamic masking. RoBERTa has outperformed BERT and other models on various benchmark tasks.
Where are Large Language Models Used?
Large language models are used in various fields, including natural language processing, chatbots, content generation, and virtual assistants.
Enhancing Customer Support
Large language models can be integrated into chatbots and virtual assistants, providing instant, accurate, and context-aware support, improving customer satisfaction and reducing response times.
Generating Content and Copywriting
These models can generate human-like text, making them valuable tools for creating content such as blog posts, social media updates, and marketing copy, saving time and boosting creativity.
Automating Text Summarization
Large language models can analyze and condense lengthy documents, articles, or reports, producing concise summaries that help users quickly grasp key points and save time.
Facilitating Machine Translation
With their advanced understanding of language structures, large language models can be used for accurate and context-aware translation between languages, enabling seamless cross-lingual communication.
Improving Sentiment Analysis and Classification
Large language models can accurately classify text by sentiment or category, helping businesses analyze customer feedback, monitor brand reputation, and gain insights into user preferences and opinions.
When to Use Large Language Models?
Streamlining Customer Interactions
Use large language models when you need to enhance customer support, create engaging chatbots, or offer personalized product recommendations, improving overall user experience.
Tackling Complex NLP Tasks
Large language models excel in handling intricate natural languages processing tasks like sentiment analysis, entity extraction, and relationship modeling, providing valuable insights for decision-making.
Boosting Content Creation
When you need to generate creative, engaging, and contextually relevant content, large language models can be invaluable tools for copywriting, blogging, and social media management.
Facilitating Multilingual Communication
Large language models are ideal for businesses operating in multiple languages, as they can provide accurate translations, cultural context, and localized content, fostering effective cross-lingual communication.
Analyzing Vast Textual Data
When dealing with large volumes of textual data, large language models can help automate tasks like summarization, classification, and anomaly detection, enabling efficient data-driven decision-making.
Best Practices For Large Language Models

Fine-tuning for Specific Domains
Customize large language models by fine-tuning them on domain-specific data, ensuring they understand the nuances, terminology, and context unique to your industry or use case.
Handling Bias and Ethical Considerations
Be aware of potential biases in large language models and implement strategies to mitigate them, such as using diverse training data and monitoring generated content for fairness and inclusivity.
Balancing Performance and Resource Requirements
Choose the appropriate model size and architecture for your needs, considering factors like computational resources, response time, and model complexity to achieve optimal performance.
Continuously Monitoring and Evaluating
Regularly assess the performance of large language models in real-world scenarios, collecting feedback from users and stakeholders to identify areas for improvement and fine-tuning.
Ensuring Data Privacy and Security
When working with large language models, be mindful of data privacy and security concerns, adhering to relevant regulations and best practices to protect sensitive information and user trust.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are large language models?
Large language models are AI-powered models, trained on massive amounts of text data, that excel in understanding and generating human-like text in various languages.
How do large language models work?
These models use deep learning and neural networks to learn patterns, structures, and relationships in text, enabling them to generate contextually relevant and coherent responses.
What are some popular large language models?
Popular large language models include OpenAI's GPT-3, Google's BERT, and Facebook's RoBERTa, which have set new benchmarks in natural language processing tasks.
What are the applications of large language models?
Applications include text generation, summarization, translation, sentiment analysis, question-answering, and conversation, spanning industries like healthcare, finance, marketing, and customer support.
What are the limitations of large language models?
Limitations include potential biases, high computational requirements, lack of interpretability, and occasional generation of irrelevant or nonsensical responses.