What is GDPR?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a comprehensive data protection law that came into effect on May 25, 2018, in the European Union (EU).
It aims to provide individuals with more significant control over their personal data while ensuring transparency and accountability from organizations that process personal data.
GDPR is built upon and replaces the 1995 Data Protection Directive (Directive 95/46/EC), which previously governed data privacy within European countries.
It has been conceived and developed over the years to address the significant data privacy concerns that came with technological advancements and the rise of the digital economy.
With GDPR in place, organizations handling personal data are now bound to adhere to strict data protection guidelines and citizens of the EU benefit from enhanced data protection rights.
This regulation has become a benchmark for global data protection laws. The GDPR applies not only to businesses located within the EU but also to entities outside the EU that process the personal data of EU residents, making its impact far-reaching and truly international.
GDPR: Key Components
"Personal data" equals any information that can point directly or indirectly to a person.
So, your name, email ID, identification number, location coordinates, or even your device's IP address falls under this.

Who's the “Data Subject” and “Data Controller"?
If you're a person whose personal data is being processed, you're the "data subject." And the one or the institution governing how and why your data is being processed – they're the "data controller."
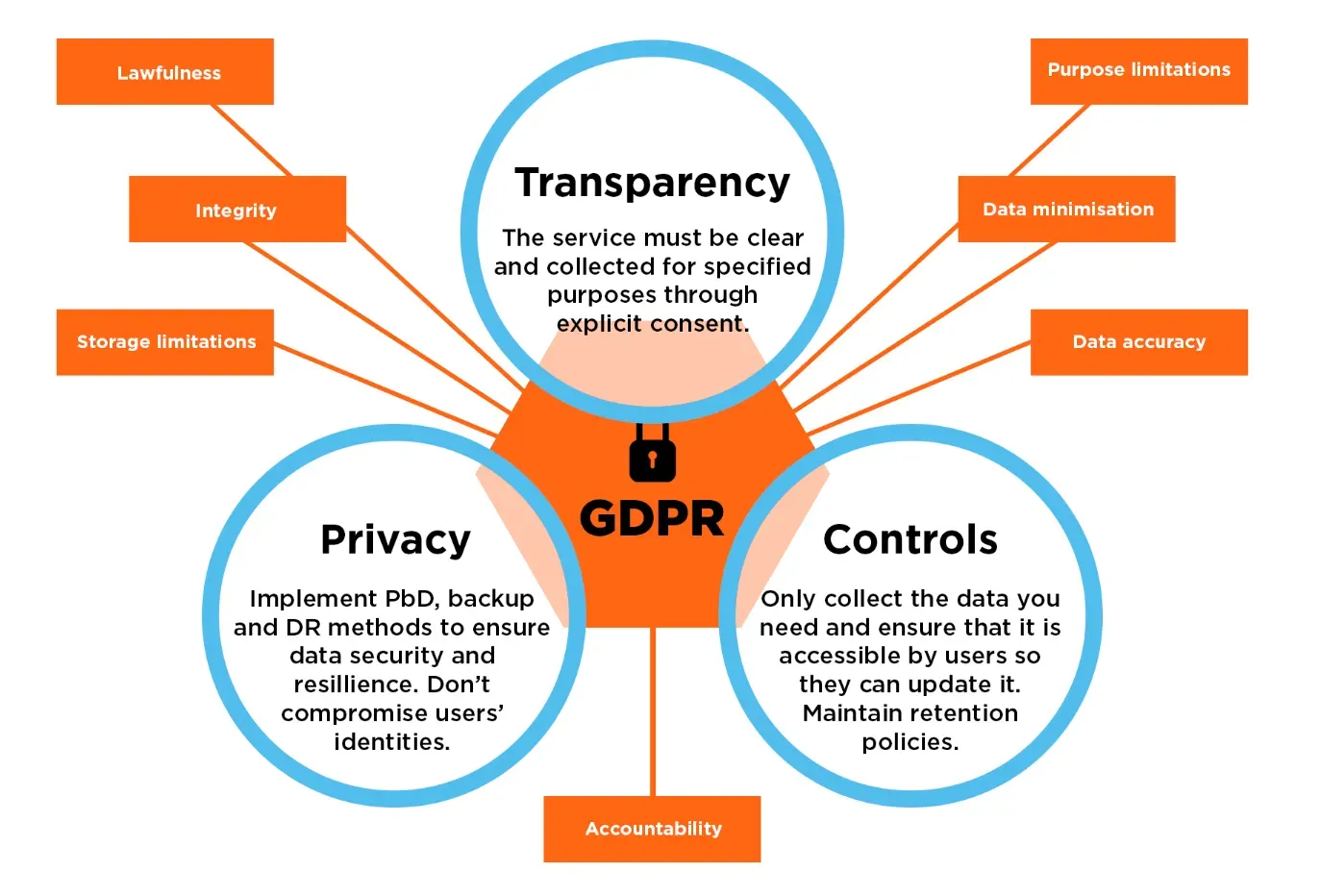
Principles of GDPR
Our super-protector, GDPR, wields seven principles as its superhero gear; these include lawfulness, fairness, transparency, purpose limitation, data minimization, accuracy, storage limitation, integrity/confidentiality (security), and accountability.
Rights of Data Subjects: Your Superpowers
As a data subject, GDPR gifts you several rights. You've got the right to access, correct ("rectification"), erase ("right to be forgotten"), limit processing, portability of data, objection, and an important one - the right not to be subject to decisions made solely through automated processing (even profiling).
The Path to GDPR Compliance
GDPR wants companies to breathe privacy - right from when they define their business processes and system designs to setting privacy as the baseline for their services and products. It's all about making privacy an integral part of every digital weave!
Undergoing a DPIA becomes a must-do for organizations when they delve into high-risk data-processing activities.
DPIAs are like a map guiding them to spot, measure, and tone down potential privacy risks.
Experienced a data breach? GDPR strictly instructs organizations to report about it to the supervisory authority within 72 hours of the realization, provided the breach could threaten individual rights and freedoms.
GDPR mandates certain organizations to appoint a DPO, who's like a captain steering the company's GDPR compliance ship, coordinating with the supervisory authority, and also an accessible point for data subjects.
Rules and Repercussions: GDPR Enforcement
Every EU member state has its team of guardians, called Data Protection Authorities, supervising GDPR enforcement nationally.
United, these teams lead the European Data Protection Board (EDPB), ensuring GDPR's consistent enforcement across the EU.
The Price to Pay: Fines for Non-Compliance
Step out of line, and GDPR imposes serious penalties, that could get up to 4% of the global annual turnover or €20 million of the breaching organization, depending on which hurts more.
The Fine Metrics
Not all breaches are repeated offenders; some are accidental! GDPR gets that and hence determines fines based on factors like nature, cooperation level, past records, and whether it was an intentional or unknowing misstep.
GDPR Enforcement and Guidance
While national DPAs lead enforcement efforts, the EDPB comes forward with advice on data protection matters, ensuring GDPR's interpretation and use are uniform all across EU countries.
GDPR as a Global Standard
Just like one superhero inspiring another, GDPR has influenced various countries to devise similar frameworks, like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and Brazil's General Data Protection Law (LGPD).
Thanks to GDPR, the EU shines bright as a global vanguard, ensuring top-notch data protection measures and vibrant data protection rights for everyone involved.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What's GDPR all about?
GDPR, standing for General Data Protection Regulation, is a robust data protection law that's active in the EU since May 25, 2018. It aims to grant individuals full control over their personal data.
Have a business outside the EU? Are you still affected by GDPR?
Absolutely! GDPR scans any organization dealing with personal data of EU residents, whether it's inside or outside the EU.
What personal rights do you possess under GDPR?
You hold quite a few solid rights such as accessing your data, rectifying it, erasing it, restricting how it's processed, porting your data, objecting to its processing, and protecting against decisions made solely via automated processing (even profiling).
Which principles does GDPR operate on?
GDPR operates on seven main principles: lawfulness, fairness, transparency; purpose limitation; data minimization; accuracy; storage limitation; integrity and confidentiality (security); and accountability.
What happens when you breach GDPR rules?
If you violate GDPR rules, you can be fined heavily - up to 4% of your global annual turnover or €20 million – whatever’s higher.