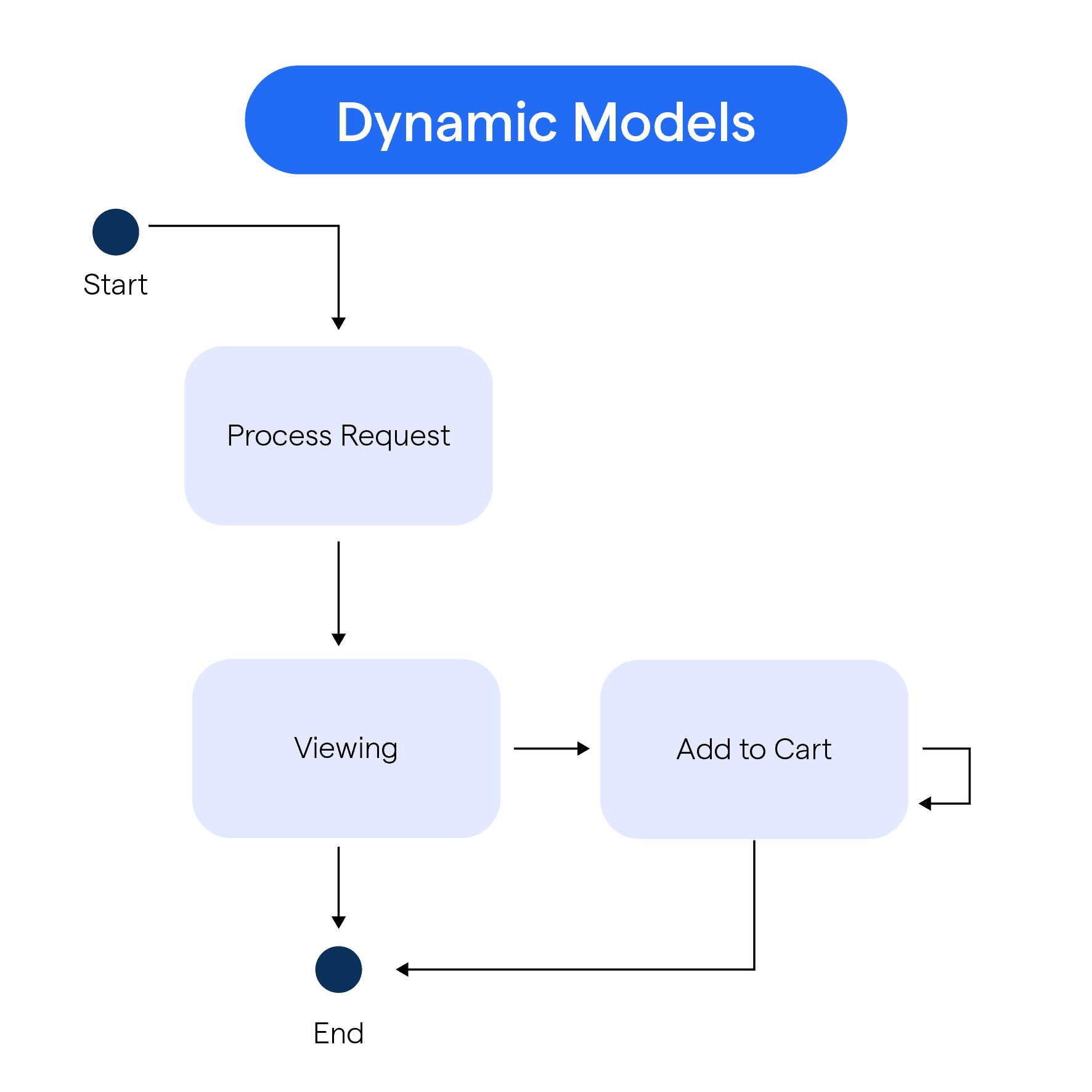
What are Dynamic Models?
Dynamic models represent the behavioral aspects of a software system - they show how different components interact and operate over time. Let's understand this with an example.
Imagine we are modeling a simple e-commerce system. The static model would show its core components like the product catalog, shopping cart, and payment processor.
But the dynamic model illustrates how these components work together when a user is shopping: the product catalog is queried, items are added to cart, shipping and tax are calculated, payment is processed, and an order confirmation is shown.
So the dynamic model captures the flow of data and operations over time, bringing the system to life! We can also use activity diagrams, sequence diagrams, and state machine diagrams to visualize the dynamic view.
In essence, static models show software structure while dynamic models demonstrate behavior. Both are crucial for thoroughly analyzing and designing complex systems and interactions upfront.
How do Dynamic Models Work?
In this section, we'll delve into how dynamic models function and their role within the realm of software development.

Concept of Dynamic Models
Dynamic models in software development are used to represent systems that evolve over time, depicting the behavior and interaction of software entities during execution.
Role in Simulating Software Behavior
Dynamic models are crucial in simulating and visualizing the intended behavior of a software system, helping developers understand how system components interact in real time.
Usage in Test Scenarios
Dynamic models enable developers to run test scenarios and evaluate the system's response, which helps in debugging and validating the system's behavior under various conditions.
Contribution to System Adaptability
Dynamic models facilitate software adaptability by allowing modifications to the system behavior during runtime, thus improving the system’s response to changing user requirements or environmental conditions.
Assistance in Decision-Making
By facilitating scenario exploration and understanding software behavior, dynamic models increasingly aid in decision-making regarding design choices, risk assessment, and system improvements.
The Role of Dynamic Models in System Modeling
In this section, we'll discuss the significance and contributions of dynamic models to the field of system modeling.
Understanding Complex Systems

Dynamic models play a crucial part in understanding and analyzing complex systems. They provide a means to examine a system's behavior over time and how it reacts to changes.
Predicting Future Behavior
Utilizing historical data, dynamic models can help to forecast a system's future behavior. This enables strategists and planners to make better-informed decisions concerning adjustments and control measures.
Simulation & Scenario Analysis

Dynamic models are essential for conducting simulations and scenario analyses. They offer valuable insights into different possibilities, aiding in risk evaluation and contingency planning.
System Optimization
Through dynamic modeling, system parameters can be tweaked to optimize performance. By observing changes in behavior over time, improvements can be more accurately targeted.
Facilitating Alignment & Communication
Dynamic models also serve as a shared language for stakeholders to understand system behavior and decision impacts. They facilitate alignment and clear communication between different functional areas.
State Diagrams in Dynamic Models
In this section, we'll investigate the critical role of state diagrams in representing and understanding dynamic systems.
- Depicting System States: State diagrams elucidate the distinct states within a system's life cycle. They offer a clear understanding of how a system transitions from one state to another under varying conditions.
- Visualizing Transitions: These diagrams visually portray the transition dynamics of a system. They highlight possible actions that result in state changes, providing deep insight into how the system evolves over time.
- Conditionally Driven Flows: State diagrams in dynamic models convey how various conditions govern the transition flow within the system.
They enable stakeholders to comprehend the case-specificity of different transitions.
- Detecting Deadlocks: State diagrams are also instrumental in identifying deadlocks or unreachable states in the system, important for unhindered system functionality and the debugging process.
- Facilitating System Design and Analysis: Last but not least, state diagrams play a pivotal role in system design, analysis, and maintenance.
They provide at-a-glance comprehension of complex systems, assisting in strategic decision-making and system enhancements.
By leveraging state diagrams in dynamic models, stakeholders are granted an accessible visual tool, allowing for intuitive understanding, optimized decision-making, and effective communication across all levels.
Components of Dynamic Models
The components of dynamic models are:
Transitions in Dynamic Models

Transitions in Dynamic Models are state changes, delineating the conditions under which these shifts happen in response to specific events or criteria.
These transitions define the cause-and-effect relationships and the direction of flow control between system states.
Events in Dynamic Models
Events in Dynamic Models are internal or external occurrences that instigate transitions between states.
Any change in system behavior or the execution of an action stems from these triggering events.
Actions in Dynamic Models
Actions in Dynamic Models encapsulate the set of tasks or operations performed by a system during a transition.
They are responses to occurrences, detailing what the system should carry out when a particular transition happens.
Guard Conditions in Dynamic Models
Guard Conditions in Dynamic Models are additional criteria linked to transitions, which control whether a transition takes place.
They act as gatekeepers, allowing the transition to occur only if the condition holds true.
Pseudostates and Activities in Dynamic Models

Pseudostates are special control nodes portraying transient states in Dynamic Models, enabling the creation of compound transitions.
Additionally, Activities describe the continuous operations performed by the system within individual states until a triggering event or condition emerges.
Generating Code and Simulating Dynamic Models
In this section, we'll delve into the process of generating code and simulating dynamic models, key steps in validating system behavior and gaining insights.
Automatic Code Generation
Generating code from dynamic models streamlines the software development process.
It promotes quicker design and implementation by converting high-level models into executable code.
Model Validation

Simulating dynamic models enables stakeholders to validate if the proposed system behaves as intended.
Through simulation, stakeholders can identify any discrepancies between the model and the actual requirements.
Sensitivity Analysis
Generating code and simulating dynamic models aid in conducting sensitivity analysis.
This allows system designers to evaluate the effects of different parameter changes and to gauge the stability of the system under varying conditions.
System Performance Evaluation
Simulation also helps in evaluating the performance of the system when subjected to external stimuli.
This enables designers to identify optimization opportunities and areas requiring improvement.
Iterative Development
Generating code and simulating dynamic models support an iterative development process, allowing for step-by-step refinement of the system and continuous enhancements as new insights emerge, leading to better overall outcomes.
By generating code and simulating dynamic models, designers gain valuable understanding and control over the targeted system's behavior, allowing them to optimize the solution prior to deployment, and to further refine it based on ever-evolving requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are dynamic models used for in system modeling?
Dynamic models are used to capture and analyze the behavior of a system over time. They help in understanding system responses to events and identifying potential issues in the system's design.
How do state diagrams represent the states and transitions in a system?
State diagrams use nodes to represent states and directed edges to represent transitions between states. Each node represents a specific state, and each transition indicates a change from one state to another in response to an event or condition.
What are events in dynamic models and how do they trigger state transitions?
Events in dynamic models represent occurrences or stimuli that trigger transitions between states. When an event occurs, it triggers a specific transition, leading to a change in the system's behavior or a new state.
How do actions in dynamic models specify responses to events?
Actions in dynamic models define the tasks or operations that the system should perform in response to an event. They are associated with transitions and are executed when the transition occurs.
What are guard conditions in dynamic models and how do they determine transitions?
Guard conditions are conditions associated with transitions that control the occurrence of the transition. Before a transition can occur, the associated guard condition is evaluated.
If the condition is true, the transition takes place; otherwise, it is blocked.
How can state diagrams be used to generate code for dynamic models?
State diagrams can be translated into executable code using modeling tools and programming languages.
The generated code represents the behavior described in the dynamic model, enabling the implementation of the system's logic.