What are IoT Communication Protocols?
Communication protocols in IoT are the rules that devices follow when talking to each other. Think of them as the languages and customs that let gadgets share information smoothly. Without these protocols, our smart devices wouldn’t understand each other, leading to chaos.
For example, IoT communication protocols like MQTT, CoAP, and Bluetooth enable devices like Yi IoT cameras to communicate efficiently. This efficient communication is crucial for managing and understanding the vast Internet of Things (IoT) data.

Key Features of Effective Communication Protocols in IoT
Effective IoT protocols have several key features. They need to be:
- Reliable: Data should be delivered accurately and on time.
- Secure: Protecting data from hackers is vital.
- Scalable: They should handle growing amounts of data as more devices connect.
- Interoperable: Devices from different manufacturers should work together.
Why are Communication Protocols in IoT so Critical?
IoT network protocols and IoT protocols are crucial for seamless data transmission, security, and device interoperability, ensuring efficient and secure communication in IoT systems.
Ensuring Seamless Data Transmission
Without good communication protocols, data might not reach its destination. Imagine sending an important email that never arrives. Protocols ensure that messages are delivered correctly and promptly.
Enhancing Security and Privacy
Security is a big deal. IoT Protocols protect your personal data from hackers. They make sure that only the right people and devices can access sensitive information.
Improving Interoperability Between Devices
Different devices, like a smart fridge and a smart light, need to understand each other. IoT Protocols allow gadgets from various brands to work together without issues.

Who Uses IoT Communication Protocols?
IoT communication protocols are widely used across various sectors, ensuring seamless device interaction. Here are some key applications.
Applications in Smart Homes
In smart homes, these IoT protocols let your gadgets talk. Your phone tells your thermostat to adjust the temperature, and your fridge might even order groceries when you’re running low.

Industrial IoT Applications
Factories use IoT communication protocols to monitor machines. Sensors can alert workers to problems before they cause a breakdown, enhancing efficiency and safety. This predictive maintenance reduces downtime and saves costs.
Healthcare and Medical Devices
Protocols in healthcare let devices track your health and send data to your doctor. This can be life-saving. Wearable devices monitor vital signs and smart pills track medication intake, improving patient care and health outcomes.

Transportation and Smart Cities
Protocols help manage traffic lights, public transportation, and more. They make cities run smoother and safer.
How Do IoT Communication Protocols Work?
Communication protocols in IoT are essential for enabling devices to communicate seamlessly. They ensure data is exchanged accurately and efficiently across diverse networks.
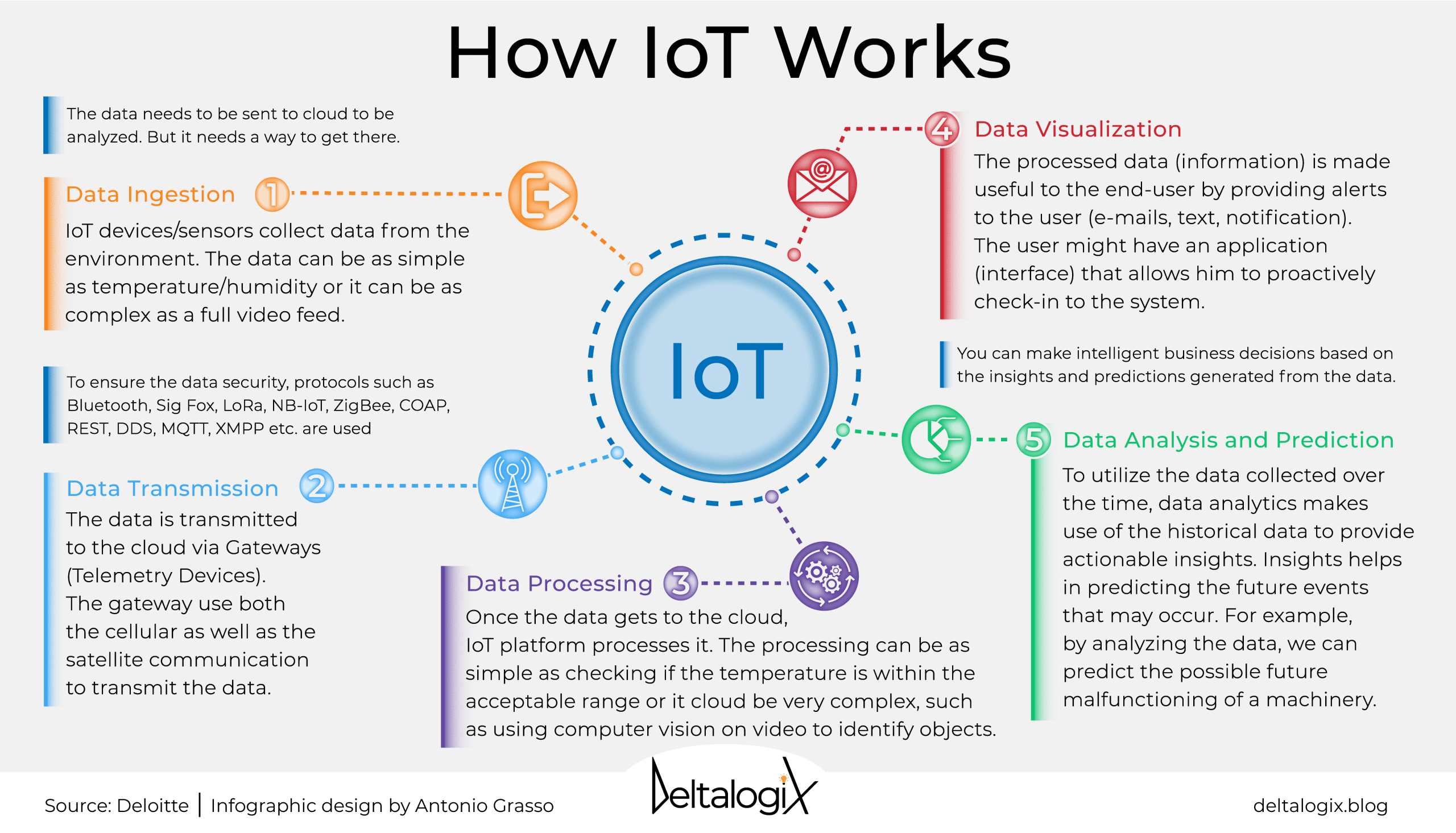
- Basics of Data Exchange in IoT Networks
Devices send data in small packets. These packets travel across networks and are reassembled at their destination.
- Role of Middleware in IoT Communication
Middleware acts as a translator between different devices. It makes sure that data is correctly formatted and understood.
- Protocol Stacks and Layered Architecture
Protocols are often part of a stack, with different layers handling different tasks. This structure makes communication more efficient and reliable.
Popular IoT Communication Protocols
Wi-Fi
Overview: Widely used for high-speed internet access in homes and businesses.
Features: Fast data transfer, broad range, easy to set up.
Pros: High bandwidth, supports many devices.
Cons: High power consumption and limited range compared to some other protocols.
Bluetooth and BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)
Overview: Common in personal devices like headphones, fitness trackers, and smart home gadgets.
Features: Short-range communication, BLE uses less power.
Pros: Low power consumption (especially BLE), simple to pair devices.
Cons: Limited range, lower data transfer speeds.
Zigbee
Overview: Designed for low-power, low-data rate applications.
Features: The mesh network is good for home automation and industrial settings.
Pros: Low power consumption, supports many devices in a network.
Cons: Lower data transfer speeds and more complex setup compared to Wi-Fi.
Z-Wave
Overview: Similar to Zigbee, it is often used in smart home systems.
Features: Mesh network operates at different frequencies to avoid Wi-Fi interference.
Pros: Reliable, low power consumption, good range.
Cons: Typically supports fewer devices in a network than Zigbee.
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport)
Overview: Lightweight protocol for low-bandwidth, high-latency networks.
Features: Publish/subscribe messaging model.
Pros: Efficient in bandwidth usage, good for constrained environments.
Cons: It requires a broker to manage messages, and security can be a concern without proper measures.
CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol)
Overview: Designed for simple electronic devices to communicate over the internet.
Features: Similar to HTTP but lighter.
Pros: Low overhead, suitable for low-power devices.
Cons: Limited features compared to more robust protocols like HTTP.
LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network)
Overview: Used for long-range communication in rural and urban areas.
Features: Low power, long range, and support for large-scale deployments.
Pros: Excellent range, low power consumption, good for remote areas.
Cons: Lower data rates, require gateways for connectivity.
NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT)
Overview: Cellular technology designed for IoT.
Features: Operates within existing cellular networks and supports deep indoor coverage.
Pros: Good range and penetration, robust connectivity.
Cons: Depending on cellular network availability, it can be more expensive than non-cellular options.
6LoWPAN (IPv6 over Low-Power Wireless Personal Area Networks)
Overview: Adapts IPv6 for use in low-power wireless networks.
Features: It integrates with existing internet protocols and has low power.
Pros: It allows for end-to-end IPv6 communication and is scalable.
Cons: Complexity in implementation requires compatibility with IPv6.
These IoT network protocols have unique strengths that suit different IoT applications. The choice of protocol depends on factors like power consumption, range, data transfer needs, and the specific requirements of the IoT system.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
What are the most commonly used communication protocols in IoT?
The most commonly used protocols in IoT include MQTT, CoAP, HTTP/HTTPS, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and LoRaWAN, each serving different connectivity and power usage needs.
How do IoT communication protocols impact device battery life?
Protocols optimized for low power consumption, such as CoAP, Bluetooth Low Energy, and Zigbee, significantly extend device battery life by reducing the amount of data transmitted and the frequency of transmissions.
What is the difference between MQTT and CoAP in IoT?
MQTT is a lightweight publish-subscribe network protocol designed for devices with limited processing power, which is ideal for mobile applications. CoAP, on the other hand, is a web transfer protocol using a request/response model that is more suited for constrained devices.
Why is security important in IoT communication protocols?
Security in IoT communication protocols is crucial to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, prevent device manipulation, and ensure data integrity, especially in applications involving personal data or critical infrastructure.
How do communication protocols in IoT impact IoT stock?
Communication protocols enhance device functionality and integration, driving demand and innovation, positively impacting IoT stock performance.
What protocols does the Yi IoT camera use?
The Yi IoT camera uses protocols like MQTT and HTTP for secure, real-time data transmission and remote monitoring.
What is the IoT meaning in smart homes?
IoT meaning in smart homes involves interconnected devices communicating via protocols to automate tasks and enhance living convenience.
What are sensor data communication protocols in IoT?
Sensor data communication protocols in IoT enable efficient, reliable, and secure transmission of data between sensors and devices within IoT networks.

