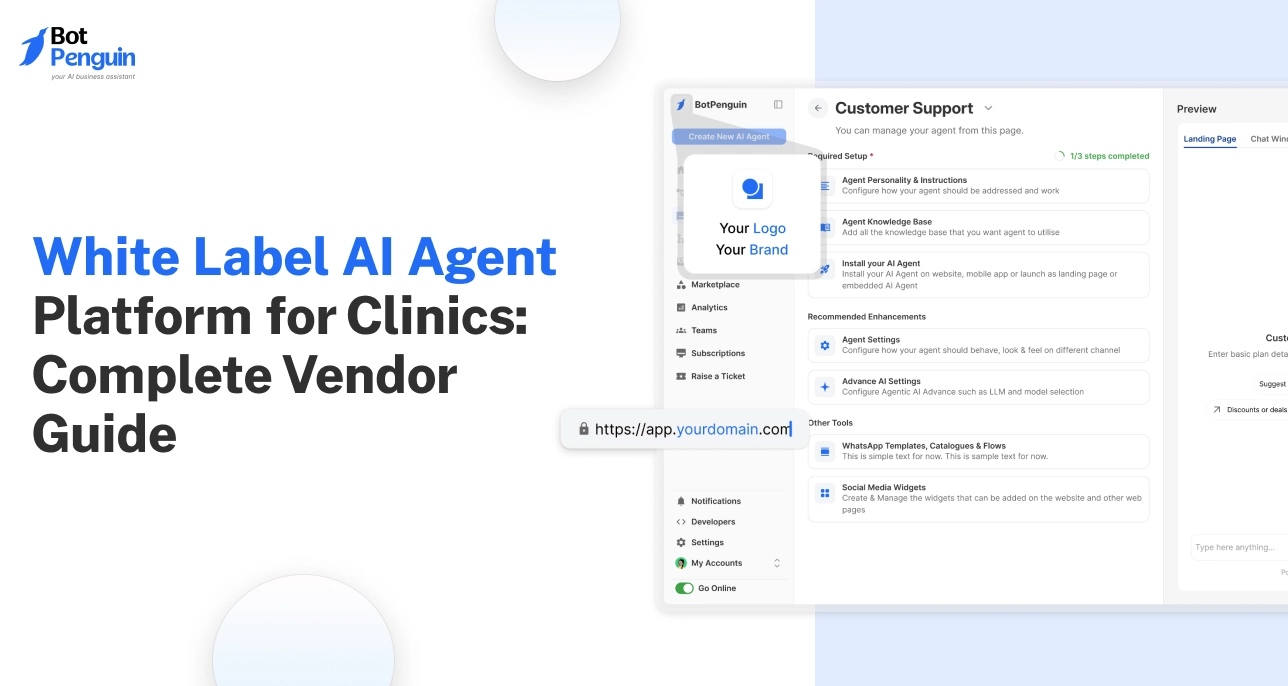
What is a Broadcast Message?
Broadcast Message is a message sent to a large audience simultaneously using a communication medium such as radio, television, or the internet.
There are three Broadcast Messages: Unicast, Multicast, and Broadcast.
Unicast is a one-to-one message transmission, while Multicast is a one-to-many transmission to a group of recipients. Broadcast, on the other hand, is a one-to-all transmission to every recipient within the communication range.
Why do we use Broadcast Messages?
Broadcast Messages offer several benefits, such as wider reach, faster delivery, and more reliable communication. It's useful for emergency alerts, business communication, social media platforms, and news broadcasting.
For instance, when there's a natural disaster or a public safety threat, Broadcast Message enables authorities to alert citizens quickly and efficiently.
Businesses can use Broadcast Messages to announce new products or services, promotions, or any changes in their operations.
How Does Broadcast Message Work?
Broadcast Message works by transmitting a message from a sender to multiple recipients using a communication medium. The technical aspects of Broadcast Messages involve transmission and reception.
1. Transmission
Transmission is sending a message from a sender to a recipient. The sender encodes the message into a format that can be transmitted through communication. T
he format of the message depends on the medium used.
For instance, radio broadcasting uses frequency modulation (FM) or amplitude modulation (AM) to transmit signals. In contrast, television broadcasting uses analog or digital signals to transmit video and audio content.
Internet broadcasting uses streaming technologies to deliver content over the internet.
Real-Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP) and HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) are the most common streaming technologies. RTMP is a real-time protocol that allows low-latency communication between the sender and the recipient. HLS, however, is a protocol that allows adaptive media streaming over HTTP.
2. Reception
Reception is the process of receiving and decoding the message by the recipient. The recipient must have the appropriate equipment to receive the message.
For example, radio receivers are used to receive radio signals. In contrast, televisions and computers are used to receive television and internet broadcasts.
The equipment that receives the message converts the transmitted signals into a format that humans can understand. The decoding process depends on the format of the message. For instance, radio receivers decode FM or AM signals, while televisions and computers decode analog or digital signals.
Broadcasting Protocols
Broadcasting protocols are communication protocols that enable the transmission of data from one source to multiple destinations.
In this article, we'll explore the different types of broadcasting protocols and their applications.
1. IP Multicast Protocol
The Internet Protocol (IP) multicast protocol transmits data from one source to multiple destinations over a network.
It is a one-to-many transmission method that enables the efficient data delivery to multiple recipients simultaneously. IP multicast is widely used in video and audio streaming applications.
2. Simple Service Discovery Protocol
The Simple Service Discovery Protocol (SSDP) is a network protocol for discovering and communicating between network devices.
SSDP enables devices to discover and communicate with each other, making it easier to set up and manage networked devices. SSDP is commonly used in home automation and Internet of Things (IoT) applications.
3. Real-time Transport Protocol
The Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) is a network protocol that transmits audio and video data over IP networks.
RTP is used in video conferencing, live streaming, and online gaming applications. RTP is designed to ensure the timely and reliable delivery of data, making it suitable for real-time applications.
4. Simple Network Management Protocol
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) manages and monitors network devices.
SNMP enables network administrators to monitor network performance, diagnose problems, and manage network devices remotely. SNMP is widely used in enterprise networks and data centers.
5. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network protocol used to automatically assign IP addresses to network devices.
DHCP makes it easier to manage IP addresses and reduces the risk of conflicts. DHCP is widely used in enterprise networks and home networks.
6. Address Resolution Protocol
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a network protocol that maps an IP address to a physical address.
ARP enables devices on a network to communicate with each other by identifying the physical address associated with an IP address. ARP is commonly used in local area networks (LANs).
7. Internet Group Management Protocol
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is a network protocol used to manage IP multicast groups.
IGMP enables devices on a network to join and leave multicast groups, making it easier to manage data distribution. IGMP is widely used in video and audio streaming applications.
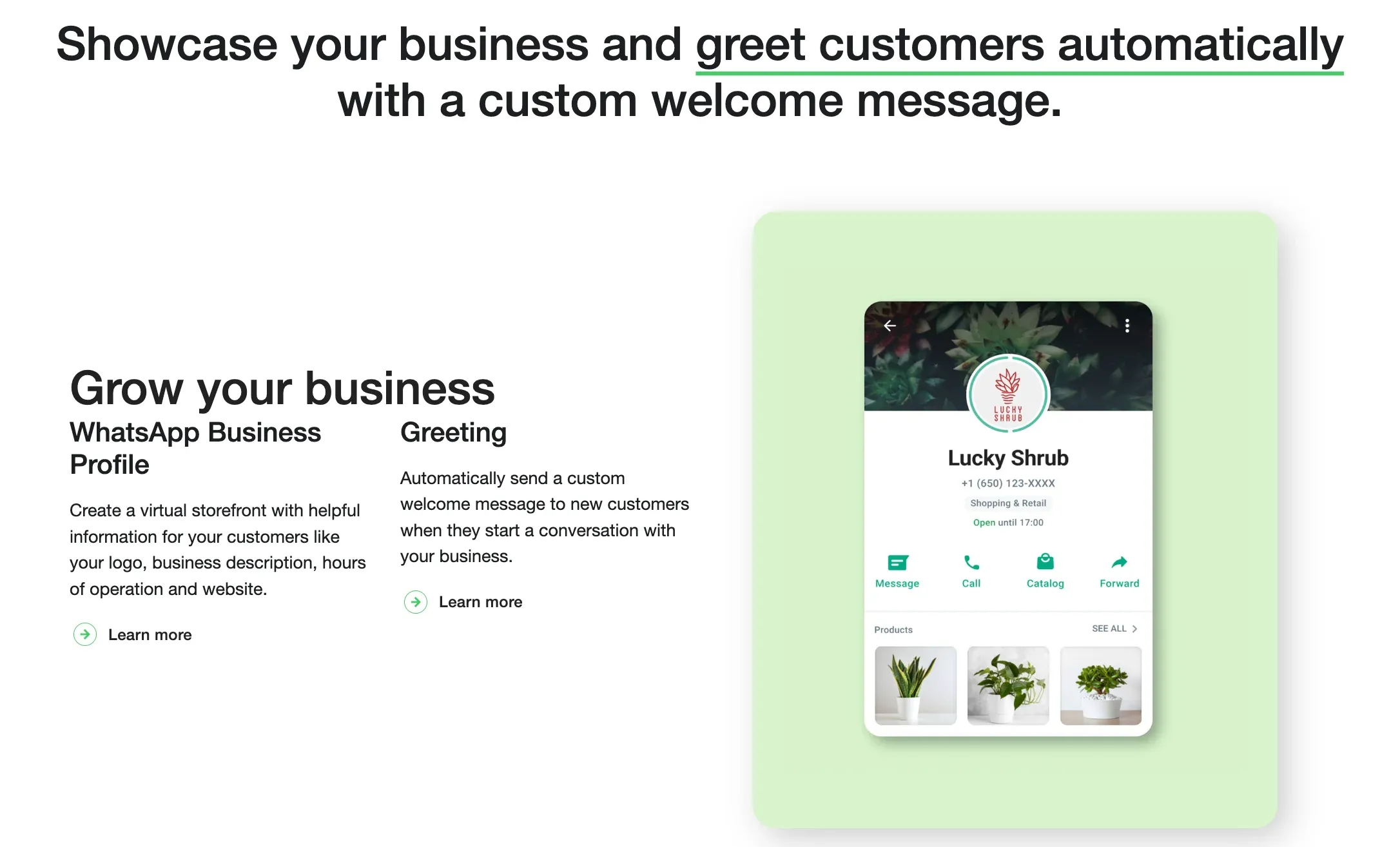
Who uses Broadcast Message?
Various industries and organizations use Broadcast Messages to communicate with their audience.
Media and entertainment, emergency services, business and corporate, and educational institutions are some industries that utilize Broadcast Messages.
For example, BBC and CNN use Broadcast Messages to reach worldwide viewers. Apple and NASA also use Broadcast Messages to announce their latest innovations and discoveries.
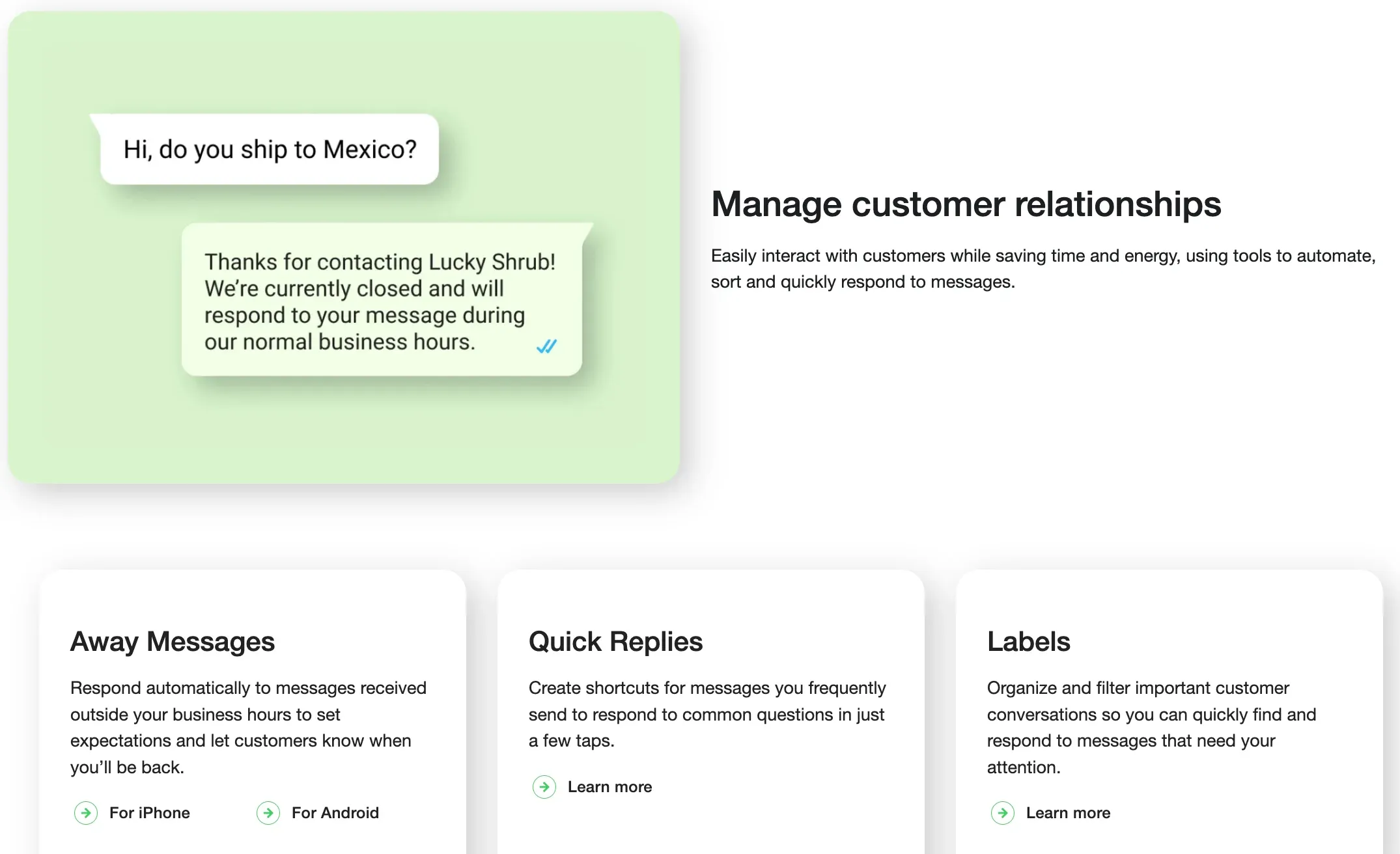
When to use Broadcast Message?
Broadcast Message is appropriate for urgent notifications, time-sensitive information, and wide-reach communication.
However, it's inappropriate for spamming, unwanted advertising, or misuse of emergency alerts.
Effective Broadcast Message requires clear, concise messaging, a targeted audience, and relevant information.
Best Practices for Broadcasting Message
Effective broadcasting requires careful planning and execution. Here are some key best practices:
1. Clear and Concise Messaging
Making sure that your messaging is clear and succinct is one of the most crucial things to keep in mind when creating an effective broadcast message.
Your communication should be simple to understand and convey the intended meaning clearly.
Avoid using specialised terminology or convoluted language that your target audience might find difficult to understand. Use clear, understandable language that is simple and straightforward.
2. Targeted Audience
Making sure you are targeting the appropriate audience is another essential component of a successful broadcast message. Depending on the message's nature, the audience may change, so it's critical to specify who your message is intended for before distributing it.
You should send an emergency alert, for instance, to those who will be most directly impacted by the situation. If it is a business announcement, the target audience should be the company's stakeholders, customers, and employees.
By selecting the appropriate audience, you can make sure that the people who need to hear your message do so, decreasing the likelihood that it will be ignored or deleted.
3. Relevant Information
Your Broadcast Message should contain relevant, useful, and valuable information for the recipients. The information should be timely, accurate, and up-to-date. Avoid sending information that is outdated, irrelevant, or redundant.
If it's a business announcement, ensure the information relates to the company's operations, products, or services. If it's a social media platform, ensure the information is related to its features or updates.
By providing relevant information, you can increase the chances of your message being read and acted upon.
4. Timing and Frequency
Information that is pertinent, useful, and valuable to the recipients should be included in your broadcast message. The data should be current, accurate, and timely. Sending out information that is stale, pointless, or redundant is best avoided.
If it's a business announcement, make sure the details are pertinent to the activities, offerings, or services of the company. Make sure the information is relevant to the platform's features or updates if it's a social media one.
You can increase the likelihood that your message will be read and taken seriously by including pertinent information.
5. Feedback and Response
A broadcast message's effectiveness depends on feedback and response. It's crucial to give recipients a chance to respond to the message or offer feedback. By doing this, you can evaluate the message's effectiveness and make any necessary modifications.
Providing feedback, such as a survey or a contact email, can help you understand the recipients' reaction to the message, for example, if it's a business announcement. Including a comment section on a social media platform can help you understand the users' opinions and reactions to the message.
You can increase the message's impact and forge stronger ties with the audience by offering a feedback mechanism.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are broadcast messages?
Broadcast messages are mass communication tools used to send a single message to multiple recipients simultaneously, often via email, text, or social media.
How do I create an effective broadcast message?
To create an effective broadcast message, focus on a clear, concise message, ensure relevance, and include a strong call-to-action to engage your audience.
When should I use broadcast messages?
Use broadcast messages for important announcements, promotional offers, event invitations, or updates that are relevant to a large portion of your audience.
Can I segment my audience for broadcast messages?
Segmenting your audience helps tailor your message to different groups, increasing relevance and improving engagement rates.
Are there any regulations governing broadcast messages?
Yes, depending on the medium (email, text, etc.), different regulations apply. Familiarize yourself with relevant laws to ensure compliance in your region.