What is Ambient Intelligence?
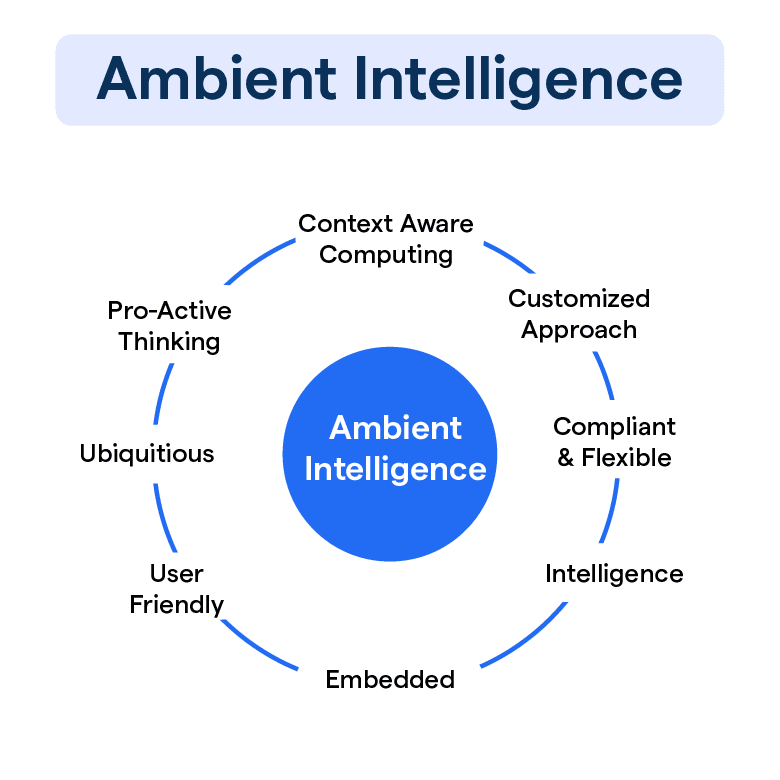
Ambient Intelligence (AML) is an emerging discipline within technology and AI that aims to create environments that are sensitive and responsive to human presence. These environments understand your preferences, anticipate your needs, and act accordingly.
The concept of AML originated in the early 2000s, pioneered by the European Commission’s Future & Emerging Technologies (FET). The growth of IoT, AI, and ubiquitous computing has bolstered AML's implementation and impact.
AML seeks to embed intelligence into our everyday environments, homes, offices, and transport, streamlining interactions and enabling seamless, personalized, and adaptive access to information and services.
By designing environments that adapt to user needs intuitively, AML significantly enhances our interactions and experience with our surrounding technology.
Elements of Ambient Intelligence
Ubiquity
In AML systems, computing devices and technologies are unobtrusively embedded in the environment, making them virtually invisible yet omnipresent — achieving 'ubiquity.'
Awareness
Awareness implies these systems' ability to perceive and understand the context, including individuals’ presence, movements, emotions, and even intentions.
Intelligence
Equipped with artificial intelligence, these environments can make informed decisions, learn from experiences and even predict and proactively respond to emerging situations.
Responsiveness
AML environments are characterized by their capability to adapt and respond to individuals' needs and preferences, delivering a unique, personalized experience.
Enabling Technologies
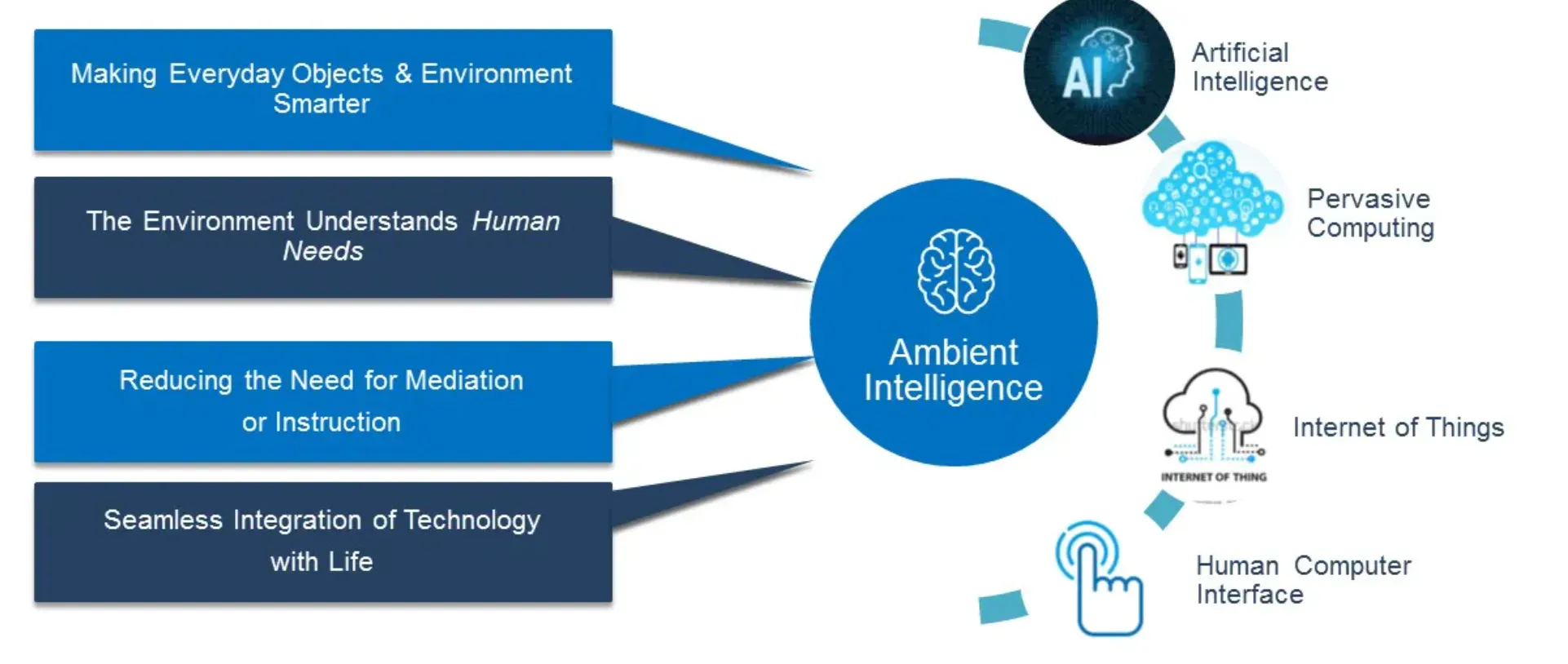
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI with machine learning provides the necessary 'intelligence' and decision-making capabilities, transforming a connected environment into an "intelligent" ambient environment.
Suggested Reading: Artificial Intelligence: Types, Future, Challenges & Applications
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT allows physical devices to connect and exchange data, enabling the creation of smart, interactive environments, a prerequisite for AML.
Suggested Reading: Internet of Things: Technologies and Challenges
Sensor Technology
Sensors provide essential data to these systems, capturing everything from temperature, light, and movement, to even biometrics.
Networking & Cloud Technologies
Networking and Cloud technologies ensure seamless data exchange and storage, enabling real-time data availability and computation for AML designs.
Deployment Areas of Ambient Intelligence
Retail and Logistics
In retail, AML can provide personalized shopping experiences. In logistics, it can automate tracking, sorting, and deliver optimized routing.
Smart Homes
Smart Homes are one of the best-known implementations of AML. They incorporate lighting, heating, electronic devices, and security systems that can respond intelligently to the occupants' habits and preferences.
Healthcare
In healthcare, AML allows continuous patient monitoring, automated reminders, emergency alerts, and even intelligent therapeutic environments.
Transportation
In transportation, AML can optimize traffic management, automate navigation, foresee emergencies, and ensure personalized in-vehicle experiences.
Challenges for Ambient Intelligence

Since AML systems continuously monitor environments and user behavior, they might trigger significant privacy concerns due to sensitive data collection and usage.
Dependability and Failure Resilience
Being embedded in our everyday lives, system reliability is crucial. AML systems should be dependable, have minimal failures, and if they occur, exhibit resilience and swift recovery.
Interoperability
With AML, we're dealing with many devices from different manufacturers. Universal standards and protocols for seamless interoperability pose a challenge.
User Acceptance
The success of AML greatly depends on end-user acceptance. Overcoming fear of technology, ensuring intuitive interactions, and guaranteeing benefits will foster wider adoption.
Privacy and Ethics in Ambient Intelligence
Data Security
AML systems host a wealth of information about individuals and their behavior. Ensuring this data's security and preventing unauthorized access is of utmost importance.
Information Consent
Collecting information about people's habits and preferences raises ethical concerns. Individuals must be informed about what data is being collected, how it will be used, and give due consent.
Anonymous Use
Given the privacy concerns, facilitating anonymous usage, where personal data isn't tied to specific individuals, is an ethical requirement.
User Control
While AML systems function autonomously, individuals must possess overriding control, ensuring they can manually manage and alter the system behavior if necessary.
Future Possibilities of Ambient Intelligence
Integrating AML with AR could provide a more immersive and personalized interaction with our environment, from aiding education and industry to enhancing entertainment and gameplay.

Personalized Ambient Media
Imagine media that adjusts according to the viewer – music that alters based on your mood, news that prioritizes your interests. It's possible with AML.
Smart Cities
Ambient Intelligence can play a significant role in designing Smart Cities– intelligent traffic management, energy optimization, personalized public amenities, and enhanced security.
Advancing Healthcare
With continuous advancements, AML can revolutionize healthcare — predictive health monitoring, personalized therapeutic environments, advanced elderly care, and possibly a lot more.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Ambient Intelligence (AML)?
Ambient Intelligence is a digital environment that proactively but sensibly, supports people in their daily lives by assisting them smartly and unobtrusively.
How does Ambient Intelligence work?
Ambient Intelligence integrates various technologies like AI, IoT, Sensor Technology and Cloud Computing into the environment, making it aware of human presence and responsive to needs.
Where can Ambient Intelligence be used?
Ambient Intelligence can be integrated into various areas, including Smart Homes, Healthcare, Transportation, and Retail, offering personalized and intelligent services.
What are the challenges in implementing Ambient Intelligence?
Key challenges include privacy concerns due to constant user monitoring, ensuring system dependability, ensuring interoperability among various devices, and gaining user acceptance.
How does Ambient Intelligence manage privacy and ethics?
AML systems ensure privacy and ethics by adhering strictly to data security standards, informing individuals about data usage and gaining consent, allowing anonymous use, and ensuring user control over the system.