What is Proof of Concept?
A proof of concept (POC) is a small exercise to test the potential of a technology or concept before investing significant time and resources into fully developing it. It's like a trial run to evaluate potential and uncover any limitations.
Let's say you have an idea for a new mobile app. Instead of diving headfirst into full app development, you can first create a simplified POC.
Build a basic workflow with key features on a mobile prototype platform. Get a few people to test it out and give feedback. This acts as a POC for validation of your app concept quickly and cost-effectively.
If the POC shows promise, you can proceed to the full product build. If it uncovers major flaws, you can iterate or even discard the concept without wasting months of engineering effort.
The Benefits of Proof of Concept
POCs help reduce risk and uncertainty. They give tangible evidence that a technology is feasible and worth pursuing further.
Things like technical specifications, integration challenges, and user experience can be examined through targeted experiments.
Many companies use POCs for cutting-edge innovations like blockchain, AI, IoT, to determine real-world viability before fully committing. A successful POC doesn't guarantee validation for the final product, but it provides confidence to move forward.
Why is a Proof of Concept Important?
A Proof of Concept (POC) plays a pivotal role when adopting new technologies or methodologies.

This deep dive explores its importance and potential in establishing that a method or idea can work successfully in real-life scenarios.
- Validates Feasibility: A POC assists in substantiating that a concept has certain potential and can be developed. It verifies that the idea, when implemented, performs as expected, ensuring resources are used judiciously.
- Assesses Technical Requirements: Proof of Concept provides a platform to understand and evaluate the technical necessities. Thus helping to identify challenges that can emerge during actual implementation and validation.
- Influences Stakeholder Confidence: A successful Proof of Concept builds confidence among stakeholders. It assures them of the practical applicability of the technology or concept, facilitating their buy-in for further development.
- Minimizes Potential Risks: Risk mitigation is a significant benefit of a Proof of Concept. It uncovers practical challenges in the early stages, helping to preempt and manage the associated risks.
- Provides a Blueprint for the Full-Scale Project: A well-executed Proof of Concept can serve as a blueprint for the real project. It offers valuable insights that can be used to develop an effective framework for the final rollout.
In essence, a Proof of Concept is a vital tool in the world of project management and product development, serving as a practical, real-world validation of a concept's feasibility and effectiveness.
How to Conduct a Proof of Concept (POC)?
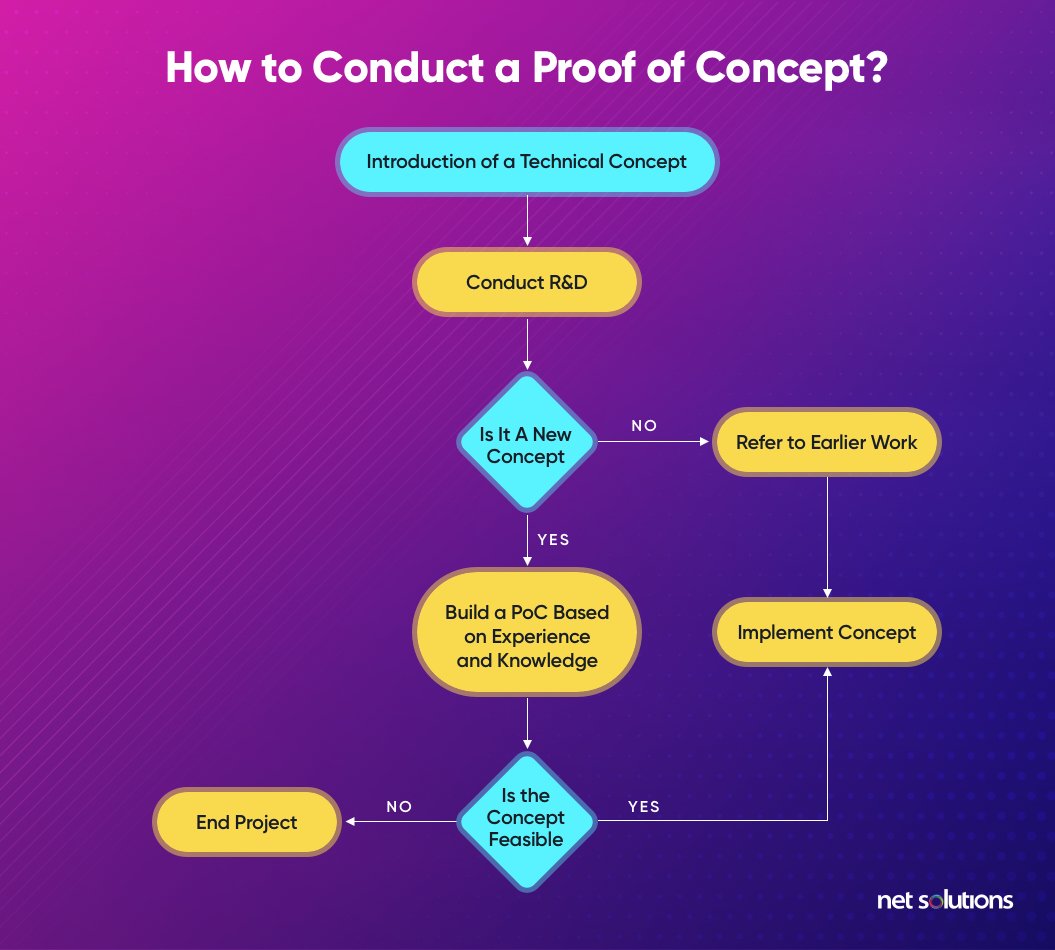
In this section, we'll delve into the step-by-step process on how to efficiently conduct a Proof of Concept to evaluate the viability and potential success of new technology, strategies, or ideas.
Step 1
Define Clear Objective
Identify the problem you're trying to solve or the business requirements you need to meet. Clearly defining your objectives for the Proof of Concept is a critical first step toward validation.
Step 2
Identify Success Criteria
Determine what success looks like for your Proof of Concept. This involves creating a set of measurable outcomes that align with your defined objectives.
Step 3
Develop a Plan
Chart out a conclusive plan outlining the necessary resources, tools, team members, and a timeline for the Proof of Concept.
This plan should detail every aspect of executing and completing the Proof of Concept.
Step 4
Execute the POC
This is the actual testing stage, where you work on the concept or the strategized solution based on your initial plan.
This could often be a scaled-down version of the final product or solution.
Step 5
Analyze and Report
Following the execution, analyze the collected data and the results based on your predefined success criteria.
Create a detailed report objectively outlining the success or shortcomings of the Proof of Concept.
Step 6
Make Informed Decisions
Based on the findings and insights drawn from your Proof of Concept, make informed decisions about whether to proceed to a full-scale implementation or revisit the solution.
Types of Proof of Concept (POC)

In this section, you’ll find the various types of proofs of concept.
- Low-Fidelity Proof of Concept: The low-fidelity Proof of Concept focuses on illustrating core conceptual elements and user flows. It uses simple mockups and prototypes for validation.
- High-Fidelity Proof of Concept: The high-fidelity Proof of Concept production-ready prototype simulating real-world behavior and functionality. It leverages actual code and interfaces.
- Technical Spike Proof of Concept: Technical spike Proof of Concept validates technical feasibility by spike testing tools, APIs, integrations, etc. It focuses on technology more than design.
- Hybrid Proof of Concept: Hybrid Proof of Concept combines a high-fidelity front-end prototype with core backend services to demonstrate a connected system.
- Exploratory Proof of Concept: An experimental Proof of Concept for early-stage concepts with minimal viability is to gauge initial customer interest and reactions.
Who Should Conduct a Proof of Concept (POC)?
In this section, you will find the mentions of who is best suited to lead a proof of concept project.
Internal Stakeholders
Key internal stakeholders like the product manager, engineering lead, or solutions architect are great candidates for leading a proof of concept.
They understand the product, tech stack, and customer needs to effectively validate feasibility.
Implementation Team
Letting the implementation team conduct the POC allows them to gain hands-on experience and identify challenges early before full-scale development. This improves solution design.
Pre-sales Engineers
Pre-sales engineers are well-equipped to demonstrate product capabilities to prospects via proof of concepts. They can build custom proofs to address prospect needs and concerns.
Third-Party Development Partners
For complex POCs involving specialized integrations, third-party development partners with related expertise, like BotPenguin, can be engaged to work on the prototype.
Customers/Prospects
In some cases, customers or prospects may collaborate on the proof of concept process to ensure the end product will meet their requirements before full investment.
When to Conduct a Proof of Concept (POC)?
In this section, we'll shed light on optimal situations where conducting a Proof of Concept (POC) is beneficial for businesses seeking to implement a new system, process, or solution.
- Evaluating New Technologies: When planning to adopt new technologies or platforms, a POC provides an opportunity to test them against your business requirements.
It allows you to evaluate the potential return on investment (ROI) before full-scale implementation.
- Testing New Business Ideas: A proof of concept is a great way to test the validation of a new business idea, product, or service in the marketplace.
It helps establish whether there’s a demand for your concept and whether it’s technically and financially plausible.
- Assessing Potential Partnerships: Before entering any partnerships, particularly in tech-related businesses, it's useful to run a POC first.
So that it will examine the fit and the value addition of the proposed partnership.
- Mitigating Risks in Major Projects: In complex or high-risk projects where significant resources are at stake, a POC can provide a measure of assurance by confirming the feasibility. Then, it will accurately estimate resource requirements of the project.
- Convincing Stakeholders: A successful POC can be crucial in persuading stakeholders, both internal and external, about the feasibility, utility, and potential success of a new initiative or strategy.
Regardless of the business type, understanding when to deploy a POC can dramatically increase the chances of success in any venture by mitigating risks, assuring stakeholders, evaluating technologies, and testing new ideas.
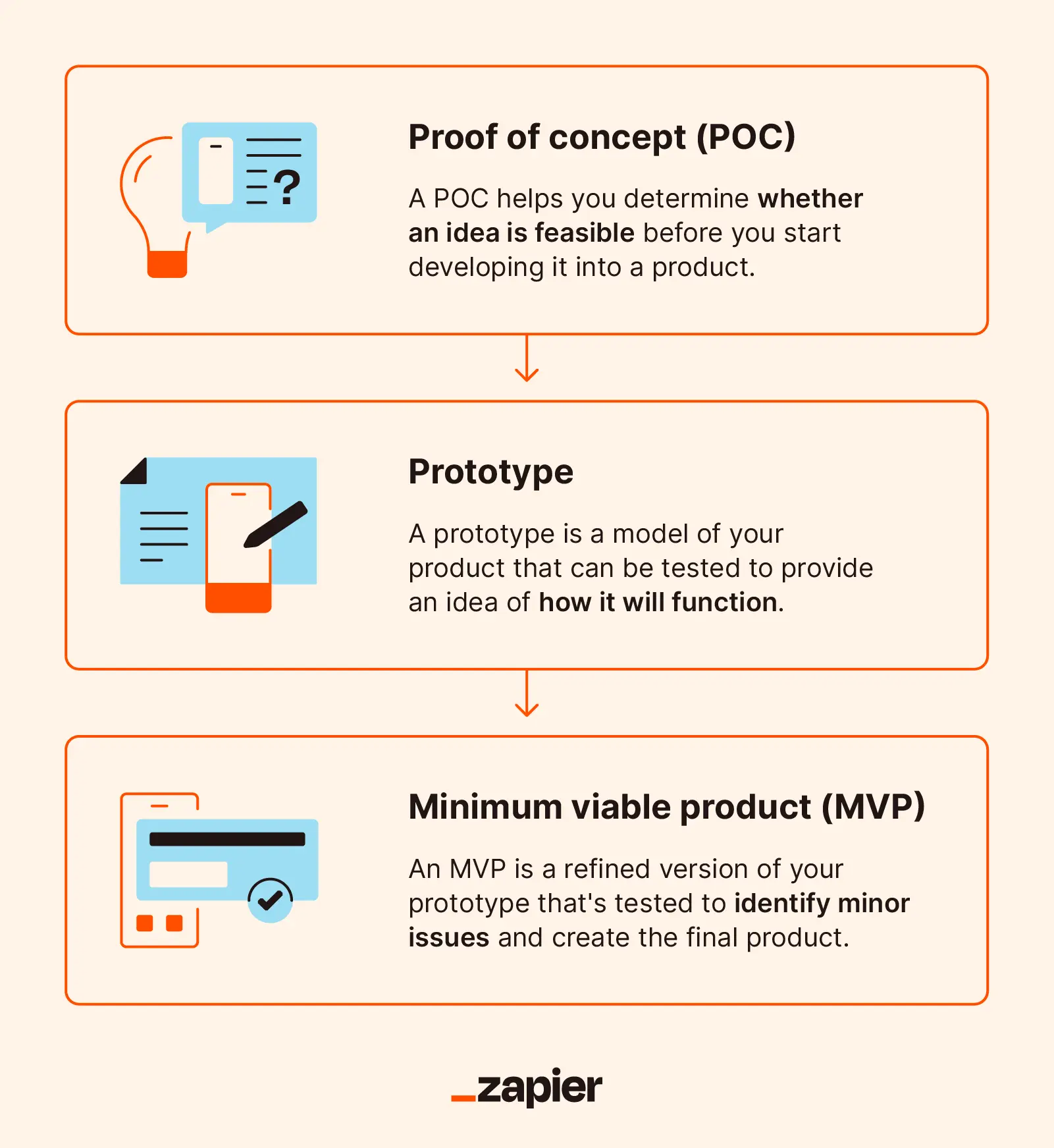
Difference Between Proof of concept (POC) and Prototype
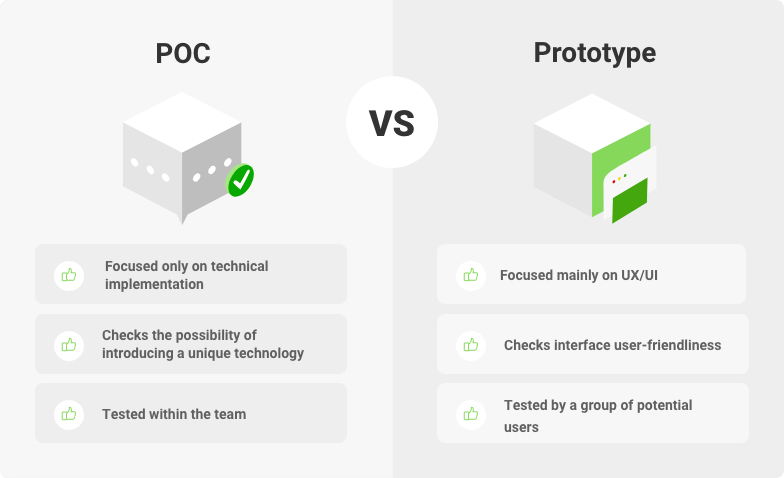
In this section, delve into the differences between a Proof of Concept (POC) and a Prototype, two key stages in product development.
- Purpose: The POC is essentially a small exercise to test a certain method or idea to verify its feasibility. Conversely, a Prototype is an early working model built to test a concept or process and understand its functionality.
- Complexity: Typically, a POC is simpler, focusing on one or two key aspects of the product. A Prototype, on the other hand, is generally more complex as it attempts to simulate the final product's functionality.
- Development Stage: A POC comes at a very early stage of the development process to confirm the viability of the proposed idea. A Prototype usually follows the POC and provides a clearer visualization of how the end product will work.
- Audience: A POC is mostly intended for internal review to decide whether to proceed with the idea. However, a Prototype might be shared with potential users, stakeholders, or investors for feedback.
- Outcome: The successful outcome of a Proof of Concept is the validation of the idea. Meanwhile a Prototype aims to obtain constructive feedback for refining the end product.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between a Proof of Concept and a prototype?
A Proof of Concept tests feasibility, whereas a prototype is a functioning version of the idea. A POC is the foundation of a prototype, as it determines its potential and gives validation.
What are the benefits of conducting a Proof of Concept?
The validation of a Proof of Concept helps save resources, money and minimizes risks. It also optimizes project outcomes, accelerates market entry, and identifies problems early on.
Who should conduct a Proof of Concept?
Any organization looking to test new projects, business ventures, and innovative ideas and implement them into the market can conduct a Proof of Concept.
When is the best time to conduct a Proof of Concept?
It's suitable to conduct a Proof of Concept during software development or when creating new startups. The Proof of Concept tests ideas, feasibility, and viability before implementation.
How long does a Proof of Concept take?
Proof of Concept duration is specific to the project's size. Usually, it takes a few months to a year. It's essential to set achievable deadlines and allocate sufficient resources to a Proof of Concept.