Definition of Data Governance
Data governance is all about managing and protecting data within an organization. Think of it as a set of rules and processes to ensure data is accurate, accessible, and secure. It's like having a traffic system for your data, ensuring it flows smoothly and safely.
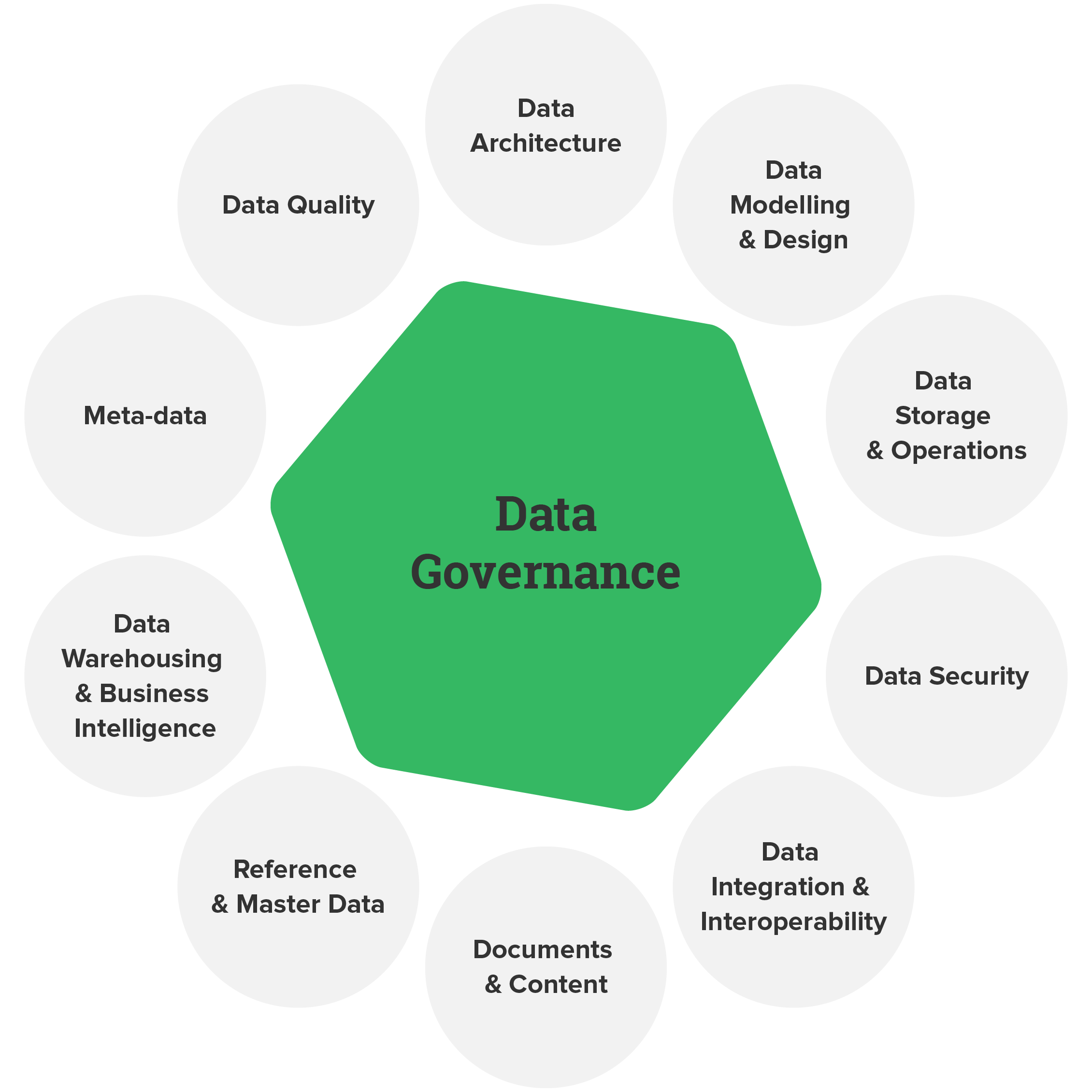
Why is Data Governance Important?
Data governance is essential because it keeps your data in check. Imagine a library without a catalog system. Finding a book would be chaos. Similarly, without data governance, managing data becomes a nightmare. It helps in making better decisions, maintaining privacy, and complying with laws.
6 Key Data Governance Tools
In this section, you’ll find the key six data governance tools.

Data Quality
First, data governance tools is data quality:
- Ensures the data is accurate and reliable.
- Regular checks and validations to maintain data integrity.
- Corrects and updates incorrect or outdated data.
Suggested Reading: Data Mining
Data Management
Next, data governance tools is data management:
- Organizes and handles data systematically.
- Includes data storage, data architecture, and data lifecycle management.
- Ensures data is easily accessible to authorized users.
Suggested Reading : Data Management Platform
Data Security
With data security, data governance software:
- Protects data from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Involves encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
- Ensures sensitive information is safeguarded.
Compliance
Compliance is the next key data governance tools that:
- Ensures data meets legal and regulatory standards.
- Keeps up with changing laws and industry regulations.
- Avoids legal penalties by adhering to compliance requirements.
Data Policies
Data policies of data governance software:
- Sets clear rules for how data is handled and shared.
- Defines roles and responsibilities for data management.
- Establishes guidelines for data usage and privacy.
Data Stewardship
Data stewardship, the last of data governance tools, assists in:
- Assigns roles for managing and overseeing data.
- Ensures accountability and responsibility for data quality and security.
- Facilitates communication between data users and data managers.
Benefits of Data Governance
In this section, you’ll find the benefits of data governance:

Improved Decision-Making
Data governance improves decision making by:
- Provides high-quality, reliable data for better insights.
- Enhances accuracy and consistency in reporting.
- Supports data-driven strategies and operations.
Enhanced Data Privacy
Data governance software enhances data privacy by:
- Protects sensitive information from breaches and misuse.
- Complies with privacy laws and regulations.
- Builds trust with customers and stakeholders.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulating compliance assist in:
- Ensures adherence to legal and industry standards.
- Reduces risk of fines and legal issues.
- Keeps the organization updated with regulatory changes.
Better Data Security
Data governance tools provide better data security through:
- Implements robust security measures to safeguard data.
- Minimizes risk of cyberattacks and data theft.
- Protects the organization’s reputation.
Increased Efficiency
With increase efficiency, you can:
- Streamlines data management processes.
- Reduces data redundancy and errors.
- Saves time and resources by improving data accessibility.
Enhanced Data Quality
Enhance data quality by data governance software can:
- Maintains accuracy, consistency, and completeness of data.
- Identifies and rectifies data quality issues promptly.
- Ensures reliable data for analysis and decision-making.
Accountability and Transparency
Accountability and transparency is another key benefits as it:
- Clearly defines roles and responsibilities for data management.
- Promotes transparency in data handling and processes.
- Enhances trust within the organization and with external parties.
Cost Savings
Cost savings is always a benefit for organizations as it can:
- Reduces costs associated with data breaches and compliance penalties.
- Optimizes resource utilization by avoiding data mismanagement.
- Improves operational efficiency, leading to financial savings.
Competitive Advantage
Data governance benefits a company by providing competitive advantages:
- Enables timely and informed business decisions.
- Provides a strategic edge by leveraging high-quality data.
- Enhances the organization’s ability to respond to market changes.
Data Governance Policies
Data governance policies are like the rules of the road for handling information. They keep everything organized and safe. Follow these:

- Start by deciding who's in charge. This person or team will oversee the whole data governance system.
- Identify what kinds of data are important to your organization. Not all data is created equal. Some are super important, and some are just nice to have.
- Figure out who gets to see what. Not everyone needs access to everything. Data access should be limited to those who need it for their job.
- Decide on how data will be stored. It needs to be kept somewhere safe and secure.
- Set rules for how data is used. This can include things like privacy rules, security measures, and how data should be shared.
- Make sure everyone knows the rules. Training and communication are key to making sure data governance policies are followed.
Frequently asked Questions(FAQs)
What is data governance and why is it important?
Data governance is managing data availability, usability, integrity, and security to ensure it's managed properly and produces consistent, trustable results.
How does data governance relate to data quality?
Data governance establishes policies and procedures to ensure high data quality across an organization.
What are the key components of a data governance program?
Key components include data stewardship, policies, standards, processes, data quality metrics, and technology.
Who should be involved in data governance efforts within an organization?
Data governance requires collaborative efforts from IT, business stakeholders, data stewards, and executive sponsors.
What challenges are commonly faced in data governance?
Common challenges include resistance to change, data ownership disputes, data silos, and lack of comprehensive policies and procedures.

