What is Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing model that provides virtualized computing resources over the Internet. With IaaS, users can access and manage essential infrastructure components such as virtual machines, storage, networks, and operating systems without having to physically maintain or invest in costly on-premises hardware.
How Does It Work?
IaaS operates on a pay-per-use or pay-as-you-go basis, offering scalability and flexibility to meet changing business needs.
With IaaS, users can easily provision and manage computing resources, allowing them to focus on application development and business growth.
Comparison to Other Cloud Computing Services
While IaaS falls under the broader umbrella of cloud computing, it is important to differentiate it from other commonly known services, such as Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS).
Unlike PaaS, which provides a pre-built platform for developers to build and deploy applications, IaaS offers a more flexible environment where users have more control over the infrastructure stack.
On the other hand, SaaS delivers ready-to-use software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for users to install and maintain software on their own devices.
Use Cases for IaaS
IaaS is widely adopted across various industries, catering to different use cases.
For example, startups and small businesses can leverage IaaS to avoid hefty upfront infrastructure costs while ensuring scalability as they grow.
Enterprises can benefit from IaaS by offloading their IT infrastructure management, reducing maintenance efforts, and improving operational efficiency.
Additionally, IaaS can support disaster recovery initiatives, enabling businesses to quickly restore their operations in the event of an unforeseen occurrence.
Why Use Infrastructure as a Service?
Scalability
IaaS allows businesses to scale their computing resources up or down as needed, accommodating fluctuating demand without the need for upfront investment in hardware.
Flexibility
Users have the freedom to choose and configure the specific infrastructure components they require, such as virtual servers, storage options, and networks, tailoring the environment to their unique needs.
Cost Efficiency
With the pay-as-you-go pricing model of IaaS, organizations only pay for the resources they use, avoiding excessive upfront expenses and the need to invest in on-premises infrastructure.
Focus on Core Competencies
By offloading infrastructure management to the IaaS provider, organizations can focus on their core competencies rather than spending time and resources on hardware maintenance and administration.
Global Availability
IaaS providers have data centers in multiple regions worldwide, allowing businesses to deploy their applications closer to their target audience, improving performance and reducing latency.
Collaborative and Agile Development
IaaS supports agile development practices, facilitating team collaboration and simplifying the deployment of new applications or updates.
Cost Management and Pricing Considerations for IaaS
IaaS helps mitigate upfront capital expenditures, as users only pay for the computing resources they consume.
The pay-as-you-go model allows businesses to scale without heavy investments in hardware.
Furthermore, IaaS providers often offer tiered pricing plans and cost optimization tools to help organizations optimize their cloud spending and avoid unnecessary expenses.
Examples of IaaS
Some of the well-known IaaS providers in the market include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Engine, and IBM Cloud.
These platforms offer a wide range of services and features tailored to meet the diverse needs of businesses across different verticals.
Who Would Use Infrastructure as a Service?
Target Audience for IaaS
IaaS appeals to a broad range of users, including startups, small and medium-sized businesses, and large enterprises.
Whether you're a tech-savvy entrepreneur with limited resources or a CTO of a multinational corporation, IaaS can bring value to your organization by providing scalable and cost-effective computing resources.
Use Cases in Different Industries
Various industries benefit from implementing IaaS in their operations.
Retailers can leverage IaaS to handle sudden spikes in traffic during peak shopping seasons, ensuring a seamless customer experience.
Healthcare providers can securely store and process patient data using IaaS, adhering to strict compliance and privacy regulations.
The possibilities of IaaS are endless, extending its advantages to sectors such as finance, e-commerce, media, and more.
How Does Infrastructure as a Service Work?
Virtualization
The underlying technology behind Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is virtualization. Virtualization allows physical infrastructure, such as servers, storage, and networking, to be divided into multiple virtual instances. These virtual instances can then be allocated to users as needed.
Cloud Management
IaaS platforms are typically managed through a centralized cloud management system. This system allows users to easily provision, manage, and monitor their virtual infrastructure. Users can access the management system through a web-based interface or application programming interface (API).
Resource Provisioning
With IaaS, users can provision computing resources on-demand. This includes virtual machines (VMs), storage, and networking. Users can choose the type and quantity of resources they need, and the IaaS provider will allocate and provision them accordingly. The resources are typically provided in a pay-as-you-go model, allowing users to only pay for what they use.
Scalability and Elasticity
IaaS offers scalability and elasticity, enabling users to easily scale their computing resources based on their needs. Users can adjust the number of VMs, storage capacity, and network bandwidth as required. This scalability ensures that businesses can handle increases in workload or traffic without experiencing performance issues.
Self-Service and Automation
IaaS platforms are designed to provide self-service capabilities to users. Users can provision, configure, and manage their infrastructure without needing to rely on manual intervention from IT staff. Additionally, automation plays a key role in IaaS, allowing users to automate repetitive tasks and streamline operations, resulting in increased efficiency and reduced human error.
Benefits of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
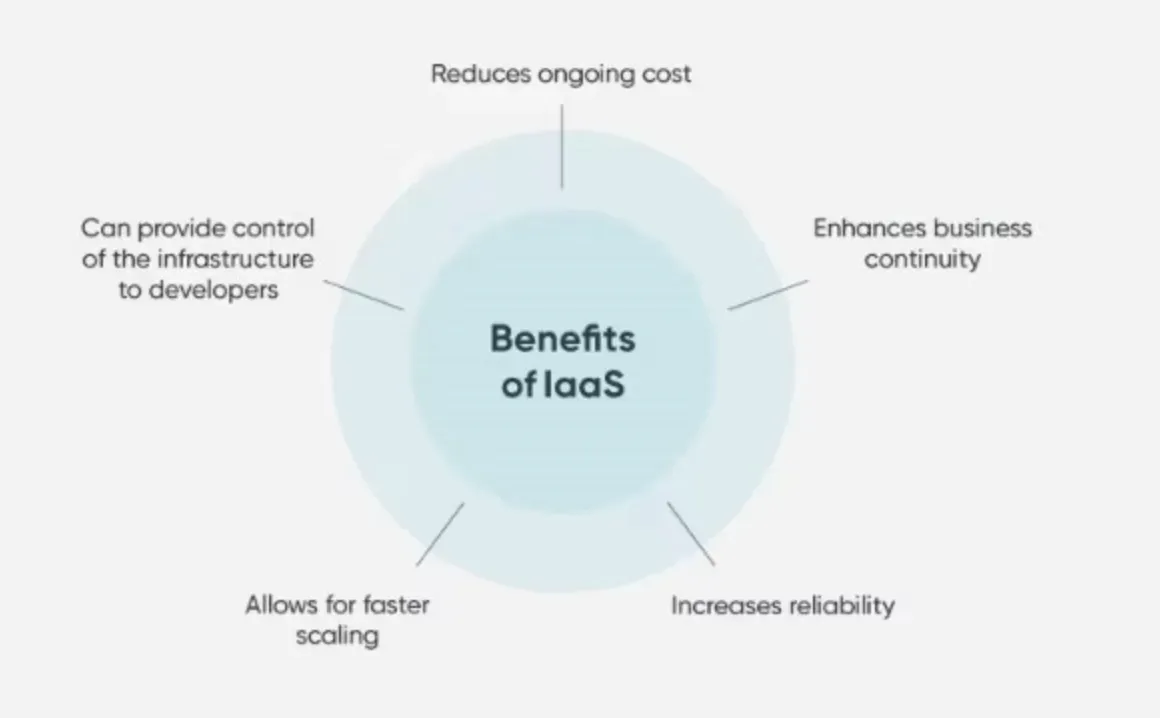
Scalability and Flexibility
IaaS allows users to quickly scale their computing resources up or down depending on their needs. This flexibility allows businesses to save money by only paying for the services they need and use, as well as easily expanding as their business grows.
Cost-effective
IaaS is a cost-effective solution for businesses as it eliminates the need for expensive hardware and maintenance costs. IaaS providers manage and maintain the infrastructure which allows businesses to focus on their core competencies rather than worrying about infrastructure.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
IaaS allows businesses to have strong disaster recovery and business continuity plans. Since all data is stored on the cloud, businesses can easily access and restore their data even in the event of a disaster at their physical locations.
Accessibility and Collaboration
IaaS allows users to access their data and applications from anywhere, at any time, as long as they have an internet connection. This feature also encourages collaboration between teams, as all members can access and work on the same files and applications in real-time.
Security and Compliance
IaaS providers take security very seriously, and their infrastructure is designed to maintain strict security protocols and comply with various regulations. This makes it easier for businesses to ensure that their data is secure and in compliance with industry regulations and standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can you migrate my existing applications and data to IaaS?
Yes, with IaaS, you can migrate your existing applications and data to the cloud. IaaS providers offer tools and resources to assist in the migration process, ensuring minimal disruption to your business operations.
Does using IaaS mean you no longer need an IT team?
While IaaS takes care of the underlying infrastructure, you still need an IT team to manage and configure your virtual environment, monitor performance, and ensure security and compliance with your applications and data.
How does billing work in IaaS?
IaaS providers typically offer a pay-as-you-go model, where you are billed based on your actual usage of resources like virtual machines, storage, and network bandwidth. This provides cost efficiency and flexibility.
Can you customize my virtual infrastructure in IaaS?
Yes, IaaS allows you to customize your virtual infrastructure by selecting the type of resources you need, such as the operating system, storage capacity, and network configurations, to meet the specific requirements of your applications.
What happens if there is a hardware failure in the IaaS environment?
IaaS providers have redundant infrastructure to minimize the impact of hardware failures. They employ various techniques, such as data replication and automatic failover, to ensure high availability and reliability for your applications and data.