Introduction
Pricing optimization is imperative for boosting profits, as a 1% price increase can increase operating profit by 11% (McKinsey, 2020). However, only 23% of businesses leverage data and analytics when making pricing decisions (Deloitte, 2021). This represents a missed opportunity, as optimized pricing strategies underpin commercial success.
Setting the right prices is complicated amid dynamic consumer demand and competition. Advances in analytics and price optimization software aim to solve this complexity.
Global spend in Price Optimization and Management solutions is projected to reach $4 billion by 2027, evidencing the prioritization to leverage data (Grand View Research, 2022). Researchers also note a 16% revenue upside for companies utilizing scientific pricing models (Forbes, 2021).
The most successful brands conduct continuous price testing, monitor market signals, and build advanced models optimizing for key outcomes.
While psychology, prestige perceptions and emotions influence consumers, data-backed experimentation and automation make the art of pricing increasingly scientific.
When coupled with value-based messaging, optimized pricing can elevate willingness-to-pay while boosting margins substantially. Now more than ever pricing excellence depends on analytics and technology to keep ahead of markets and drive growth.
So continue reading to know more about strategies for successful product marketing and pricing.
What is a Product Marketing Strategy?
Launching a product successfully requires much more than just having a great idea or prototype. Be it a physical gadget, SaaS platform or consumer app, a well-defined strategy aligned to market realities holds the key to adoption and growth.
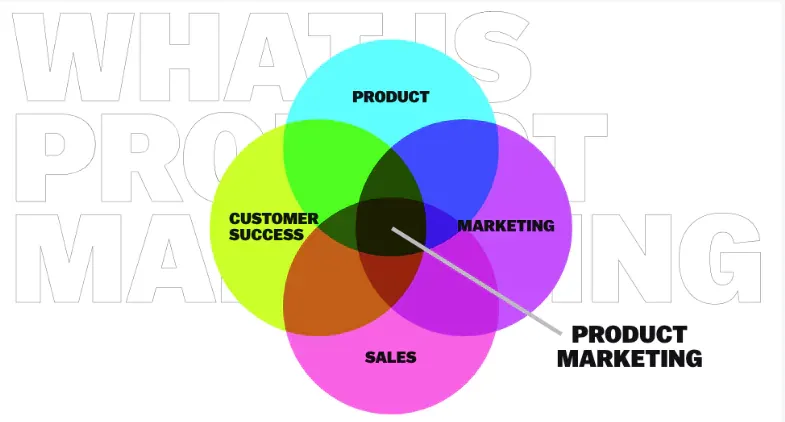
This is where an insightful product marketing plan spelling out positioning, pricing, placement and promotional strategies creates immense value.
Key Features of Product Marketing Strategy
Let us consider key components that must feature in every results-driven product go-to-market blueprint:
Comprehensive Market Analysis
Basis all strategic decisions is a detailed understanding of the target market. Analyzing size, growth patterns, competition analysis, customer personas and sales cycle benchmarks allows creating tailored strategies.
Appropriate Segmentation & Positioning
Grouping prospective customers exhibiting similar needs-behavior patterns allows appropriate messaging.
Positioning refers to shaping how the product resonates with priority segments - whether through cheaper pricing, durability or exclusive features etc.
Impactful Pricing Decisions
Pricing lever plays an influential role in adoption. Price too high, losing out bottom funnel customers while going too low leaves money on the table.
Pricing must balance customer perception of product's value against ability to pay. Models like per user license, one-time or usage-based billing merit close evaluation.
Multi-Channel Sales & Distribution
Relying on only one channel - be it online stores or retail outlets leads to limited reach. Having the right product available across relevant customer touch points through modern trade, online marketplaces, dedicated sales force etc. maximizes visibility.
Results-Focused Promotions Mix
Catchy ads alone don't translate into revenues. Tailored messaging focused on product's benefits for the defined target group via relevant digital and offline media achieves better ROI.
Tools like free trials, content marketing and referrals incentivize product experience driving conversions.
The product marketing mix thus requires all elements - positioning, product, pricing, placement and promotions to work cohesively to enable sales and business growth.
How to Create a Product Marketing Strategy
Creating an effective product marketing strategy requires careful planning and consideration of various elements. Here are the steps to follow:
Step 1
Define Your Target Customers
Identify the specific group of customers you want to target with your product. This involves understanding their demographics, preferences, needs, and pain points. Conduct market research, analyze customer data, and gather insights to create buyer personas, which will guide your marketing decisions.
Step 2
Understand the Market
Thoroughly research the market to gain insights into industry trends, competitors, and customer expectations. It's essential for product marketing.
Assess the market size, growth potential, and any gaps or opportunities that your product can fill. Understanding the market dynamics will help you position your product effectively and set realistic pricing strategies.
Step 3
Determine the Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
This is your Unique Selling Proposition (USP). Focus on what makes your product special and communicate it clearly to your target customers.
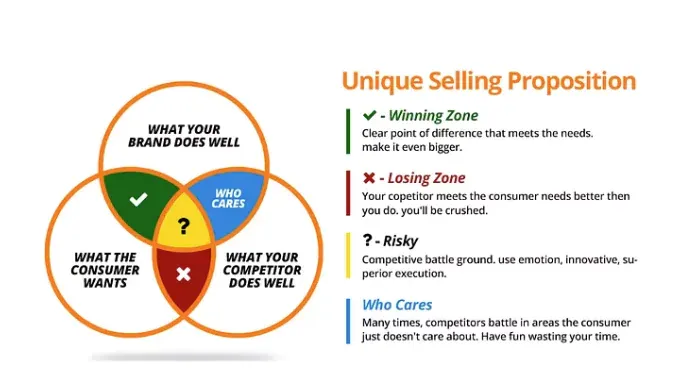
Your USP will be a key factor in pricing decisions and marketing messaging.
Step 4
Set Clear Objectives
Define clear and measurable objectives for your product marketing strategy. It is very important for product marketing.
These objectives should align with your overall business goals and should be specific, achievable, and relevant. Examples of objectives could be increasing market share, boosting sales revenue, or expanding into new markets.
Step 5
Develop Pricing Strategies
Pricing is a crucial aspect of product marketing. Determine the pricing strategies that best align with your product, target customers, and market dynamics.
Consider cost-based pricing, value-based pricing, competitive pricing, psychological pricing, or dynamic pricing based on your product's unique characteristics and competitive landscape.
Step 6
Create a Marketing Mix
Develop a comprehensive marketing mix that includes the 4Ps: product, price, place, and promotion. Define your product features, pricing strategy, distribution channels, and promotional activities. Ensure consistency across all elements of the marketing mix to create a cohesive and impactful strategy.
Step 7
Implement and Evaluate
Once your product marketing strategy is developed, it's time to implement and execute it. Monitor the performance of your marketing efforts regularly, and use data and analytics to evaluate the effectiveness of your strategy.
Make necessary adjustments and improvements based on customer feedback, market trends, and results.
Different Pricing Strategies for Product Marketing
Price lies at the intersection of product, marketing, sales and wider commercial strategy.
When optimized effectively, pricing can drive significant revenue and margin upside. However, suboptimal price-setting equally risks relinquishing market share or leaving profits on the table.
This section outlines key pricing frameworks, along with the best applications, advantages and disadvantages of each approach.
Cost-Based Pricing
With cost-based pricing, product prices are set by marking up estimated unit costs to achieve a target gross margin.
This facilitates a floor price for profitability while ensuring affordable access for cost-conscious customer segments. Despite its common use for commodity items, cost-based pricing carries disadvantages. It encourages cost-cutting corners that can diminish quality. Competitor actions also readily erode margins.
Competitor Benchmarking
Here product pricing is based on competitor offerings and market rates.
Besides conserving resources otherwise spent on analysis, this tactic reduces undercutting risks when buyers compare prices. However, competitor prices reveal little about customer perceptions and risk providers becoming commoditized on cost alone.
Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing sets product prices based on the perceived value delivered to customers, balanced against supply costs.
Though intensive research is vital to gauge perceived value accurately, this framework maximizes willingness-to-pay. Premium pricing is possible for differentiated high-value propositions. Downsides include increased subjectivity risks and smaller addressable markets than low-cost leaders.
Customer Segment Pricing
This approach charges varying prices to different customer segments based on sensitivity and ability to pay. For example, discounted academic pricing versus premium corporate packages. Perfect price discrimination boosts both revenues, by accessing a wider market, and margins.
However, inconsistent pricing can frustrate customers and requires restricting access between segments.
Promotional Pricing
Running frequent but time-limited promotions with discounted pricing is a pull strategy to stimulate sales. This risks longer-term brand equity diminution but remains popular to clear inventory, boost volumes seasonally or attract new customers through low barrier trials.
Bundling Pricing
Bundling combines several offerings into a discounted packaged price to increase value perceptions. This capitalizes on consumers that use or value some but not all items in the bundle to realize latent demand without compromising unit economics. Challenges include higher complexity and right-bundling discovery.
When strategizing pricing, no single best framework exists universally. Astute marketers balance and blend approaches based on market intelligence while testing continuously because even tiny variations can shift outcomes significantly.
This analytical method lifts pricing from guesswork art towards data-driven science with rewards to match.
Conclusion
Psychology and emotions have always factored into consumers’ willingness to pay. Meanwhile analytics and automation enable brands to rapidly test, simulate and adapt for maximized outcomes.
The most analytically mature organizations demonstrate a 19% faster revenue growth compared to lagging competitors (McKinsey, 2022). This commercial advantage will only widen as leading brands industrialize data-driven pricing supported by next-generation software solutions.
Pricing represents an outstanding opportunity to boost margins and defend market share amid turbulent markets.
By leveraging data, brands can model customer segmentation dynamics, competitive actions, market signals and willingness to pay down to granular levels.
This enables continuous optimization to stay ahead of demand shifts. With the average price change increasing profits by 7.8%, scientifically leveraging pricing’s commercial power promises year-round rewards (McKinsey, 2020).
The time for pricing excellence is now.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the key factors to consider when setting product prices?
Product marketing involves considering factors such as production costs, competition, target market demand, and perceived value.
A thorough analysis of these elements can help determine an optimal pricing strategy that maximizes profitability and maintains competitiveness within the market.
How can businesses determine the right pricing strategy for the product marketing?
Businesses can determine the appropriate pricing strategy by conducting market research, understanding consumer behavior, and analyzing competitors' pricing models.
Additionally, factors such as product differentiation, value proposition, and market positioning should be considered to devise a strategy that aligns with business objectives.
What role does consumer psychology play in pricing strategies for product marketing?
Consumer psychology significantly influences pricing strategies, as it governs how consumers perceive the value of a product.
Understanding consumer behavior, preferences, and the psychological factors that drive purchasing decisions can help businesses implement pricing strategies that resonate with their target audience, leading to increased sales and brand loyalty.
How can businesses effectively communicate the value of their pricing to customers?
Communicating the value of pricing involves emphasizing the product's unique features, benefits, and the problem it solves.
Using effective marketing channels, businesses can highlight the value proposition, customer testimonials, and comparisons with competing products, enhancing customers' understanding of the product's worth.